1 SpringBoot项目
1.1 第一个SpringBoot项目
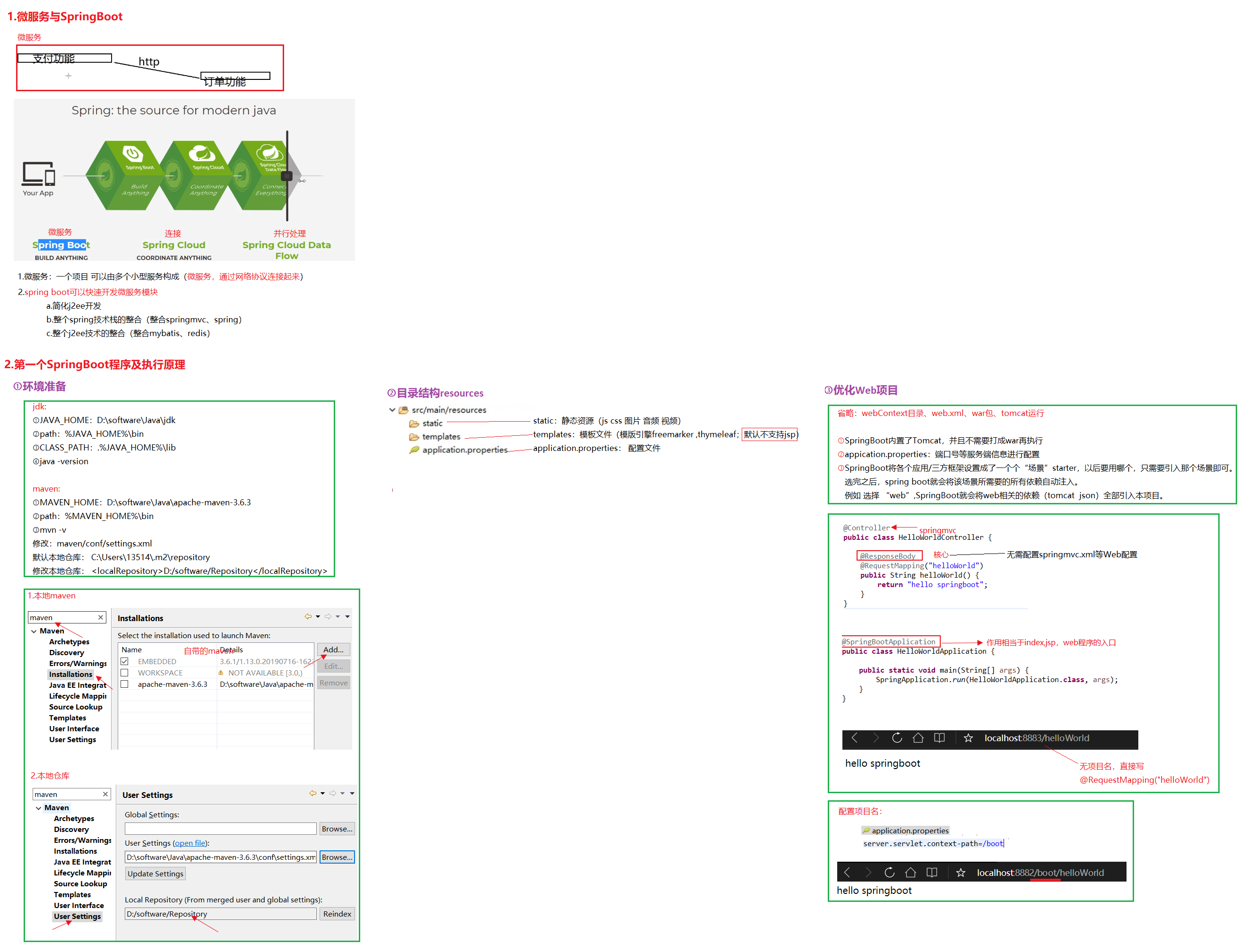
01.优化WEB项目:
省略:webContext目录、web.xml、war包、tomcati运行
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
a.SpringBoot内置了Tomcat,并且不需要打成war再执行
b.appication.properties:端口号等服务端信息进行配置
c.SpringBoot将各个应用/三方框架设置成了一个个“场景”starter,以后要用哪个,只需要引入那个场景即可。
选完之后,SpringBoot就会将该场景所需要的所有依赖自动注入。
例如选择“web”,SpringBoot就会将web相关的依赖(tomcat json)全部引入本项目。
02.自动装配
原理:约定优于配置(核心:将一些配置功能放到源码底层实现),通俗点讲,叫做“老地方见”
优点:①版本仲裁中心:引入依赖时,不用再担心版本不兼容引发的冲突问题(可能存在部分jar没引入,手动)
②场景启动器:(json.jar、tomcat.jar、hibernate-validator.jar、.spring-web.jar、) -> spring-boot-start-web
应用:@EnableAutoConfiguration,就是Springboot提供自动装配的注解
1.2 核心注解
01.SpringBoot自动装配原理:
SpringBoot通过@SpringBootApplication核心注解进行启动
@SpringBootApplication = @SpringBootConfiguration + @ComponentScan + @EnableAutoConfiguration:
其中,@SpringBootConfiguration:指定该类是SpringBoot的配置类
@ComponentScan:扫描该类所在的包下所有的类,并把符合扫描规则的类自动装配到容器
@EnableAutoConfiguration:打开自动配置的功能,也可以关闭某个自动配置的选项;
如关闭数据源配置,@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class })
根据pom.xml中依赖,自动推测出所需配置,并自动配置好。
例如,pom.xml中有spring-boot-starter-web,自动将web和SpringMVC配置好。
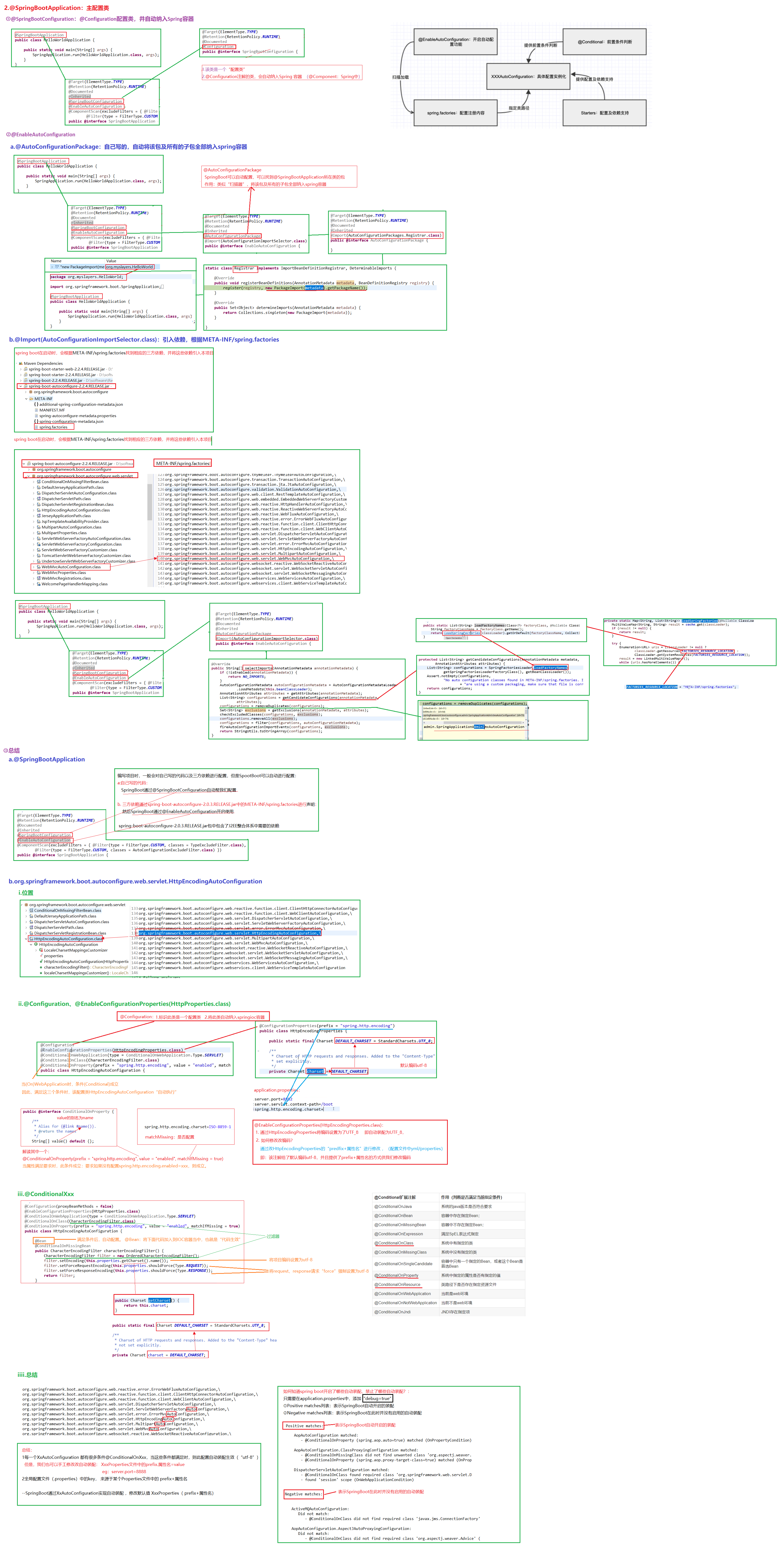
02.@SpringBootApplication:
@SpringBootConfiguration:@Configuration配置类,自动纳入Spring容器
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动化配置,也可以自定义配置代替自动化配置中的某一个配置
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自己写的,自动将该包及其所有的子包纳入Spring容器
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):自动装配META-INF/spring.factories
@ComponentScan:扫描包
@Service:业务层
@Repository:数据层
@Controller:控制层
@RestController:控制层
@Component:泛指各种组件
@value:单值注入,更加精准,而不是让Spring自动执行它
@Configuration:配置类,一般和@value组合使用
03.@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")与@value:二者可以互补使用
@ConfigurationProperties:同时绑定properties和yml方式的注值,支持批量注值
@value:支持单个注值
04.Spring、SpringMVC、SpringBoot常见注解
元注解
@Documented 将会在被此注解注解的元素的javadoc文档中列出注解,一般都打上这个注解没坏处
@Target 注解能被应用的目标元素,比如类、方法、属性、参数等等,需要仔细思考
@Retention 仅在源码保留,还是保留到编译后的字节码,还是到运行时也去加载,超过90%的应用会在运行时去解析注解进行额外的处理,所以大部分情况我们都会设置配置为RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME
@Inherited 如果子类没有定义注解的话,能自动从父类获取定义了继承属性的注解,比如Spring的@Service是没有继承特性的,但是@Transactional是有继承特性的,在OO继承体系中使用Spring注解的时候请特别注意这点,理所当然认为注解是能被子类继承的话可能会引起不必要的Bug,需要仔细斟酌是否开启继承
@Repeatable Java 8引入的特性,通过关联注解容器定义可重复注解,小小语法糖提高了代码可读性,对于元素有多个重复注解其实是很常见的事情,比如某方法可以是A角色可以访问也可以是B角色可以访问,某方法需要定时任务执行,要在A条件执行也需要在B条件执行
@Native 是否在.h头文件中生成被标记的字段,除非原生程序需要和Java程序交互,否则很少会用到这个元注解
启动注解
@SpringBootApplication 包含了@ComponentScan、@Configuration和@EnableAutoConfiguration注解
@SpringBootConfiguration 等同于spring的XML配置文件;使用Java代码可以检查类型安全
@ComponentScan 让spring Boot扫描到Configuration类并把它加入到程序上下文
@EnableAutoConfiguration 自动配置
配置导入功能:
@Configuration 等同Spring的XML配置文件,【指明该类是Bean配置的信息源】,相当于<beans></beans> 仅主类
@Bean 等同Spring的XML配置文件,【产生一个bean交给Spring管理】,相当于<bean></bean> 仅方法
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Import 导入其他配置类
@PropertySource 加载非默认配置文件的数据
@ImportResource 识别除application.properties/yml等其他配置文件,默认Springboot不识别
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Autowired 自动导入依赖的bean,byType方式,完成属性、方法的组装,对类成员变量、方法、构造函数声明
@Resource(name="name", type="type") 没有括号内内容的话,默认byName方式,作用同@Autowired
@inject 等价于默认的@Autowired,只是没有required属性
业务层功能:
@Component 泛指组件,当组件不好归类时,使用该注解
@Repository DAO层
@Service Service层
@Controller Controller层
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Controller 定义控制器类,配合注解@RequestMapping
@RestController @RestController = @ResponseBody + @Controller
@RequestMapping 提供路由信息,负责URL到Controller中的具体函数的映射
params:指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理
headers:指定request中必须包含某些指定的header值,才能让该方法处理请求
value:指定请求的实际地址,指定的地址可以是URI Template 模式
method:指定请求的method类型, GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等
consumes:指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),如application/json,text/html
produces:指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回
@ResponseBody 表示该方法的返回结果直接写入HTTP response body中,
一般在异步获取数据时使用,在使用@RequestMapping后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,
加上@ResponseBody后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP response body中
比如异步获取json数据,加上@Responsebody后,会直接返回json数据。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Value 注入 application.properties 或 application.yml 配置的属性的值
@PathVariable 路径变量,参数与大括号里的名字一样要相同
@Profiles 配置在dev、test、prod环境下生效,任何@Component或@Configuration都能被@Profiles标记
@ConfigurationProperties SpringBoot将尝试校验外部的配置,默认使用JSR-303进行校验配置
HTTP注解
@RequestBody HTTP请求获取请求体(处理复杂数据,比如JSON)
@RequestHeader HTTP请求获取请求头
@CookieValue HTTP请求获取cookie
@SessionAttribute HTTP请求获取会话
@RequestAttribute HTTP请求获取请求的Attribute中(比如过滤器和拦截器手动设置的一些临时数据),
@RequestParam HTTP请求获取请求参数(处理简单数据,键值对)
@PathVariable HTTP请求获取路径片段
@MatrixAttribute HTTP请求获取矩阵变量允许我们采用特殊的规则在URL路径后加参数(分号区分不同参数,逗号为参数增加多个值)
全局异常处理:
@ControllerAdvice 包含@Component,统一处理异常,处理控制器类抛出的所有异常
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) 用在方法上面,表示遇到这个异常就执行以下方法
其他注解
@Transient 表示该属性并非一个到数据库表的字段的映射,ORM框架将忽略该属性
@ConfigurationProperties 给对象赋值,将注解转换成对象
@RequestMapping 和请求报文是做对应的
@EnableCaching 注解驱动的缓存管理功能
@GeneratedValue 用于标注主键的生成策略,通过 strategy 属性指定
@JsonIgnore 作用是json序列化时将Java bean中的一些属性忽略掉,序列化和反序列化都受影响
@JoinColumn(name=”loginId”) 一对一:本表中指向另一个表的外键。一对多:另一个表指向本表的外键
1.3 运行原理、启动流程
01.SpringBoot核心通过Maven继承依赖关系快速整合第三方框架
a.spring-boot-starter-parent作用
指定JDK编译版本
指定UTF-8编码方式
依赖管理,继承自spring-boot-dependencies定义依赖的版本
打包支持
动态识别资源
识别插件配置
识别不同的配置,如:application-dev.properties 和 application-dev.yml
b.依赖spring-boot-starter-web能够整合Spring环境,原理通过Maven子父工程
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- SpringBoot 整合SpringMVC -->
<!-- 依赖spring-boot-starter-web能够整合Spring环境 原理通过Maven子父工程 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
c.整理过程
springboot 通过引用spring-boot-starter-web依赖,整合SpingMVC框架。当你添加了相应的starter模块,就相当于添加了相应的所有必须的依赖包,
包括spring-boot-starter(这是Spring Boot的核心启动器,包含了自动配置、日志和YAML);
spring-boot-starter-test(支持常规的测试依赖,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito以及spring-test模块);
spring-boot-starter-web (支持全栈式Web开发,包括Tomcat和spring-webmvc)等相关依赖。
02.SpringBoot自动装配原理
SpringBoot通过@SpringBootApplication核心注解进行启动
@SpringBootApplication = @SpringBootConfiguration + @ComponentScan + @EnableAutoConfiguration:
其中,@SpringBootConfiguration:指定该类是SpringBoot的配置类
@ComponentScan:扫描该类所在的包下所有的类,并把符合扫描规则的类自动装配到容器
@EnableAutoConfiguration:打开自动配置的功能,也可以关闭某个自动配置的选项;
如关闭数据源配置,@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class })
根据pom.xml中依赖,自动推测出所需配置,并自动配置好。
例如,pom.xml中有spring-boot-starter-web,自动将web和SpringMVC配置好。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
在@EnableAutoConfigration注解中,使用 @Import导入自动配置类选择器的字节码对象,可以批量载入到 Spring 容器中。
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解:
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
在AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class中有getCandidateConfigurations方法,会调用【SpringFactoryLoader读取jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories文件】
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
而spring.factories配置了自动装配的类,最后根据@Condition判断自动配置类是否符合条件,自动装配Bean
## Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
com.huangx.springboot.autoconfig.MyApplicationContextInitializer
## Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
com.huangx.springboot.autoconfig.MyApplicationListener
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
汇总:
Spring Boot通过@EnableAutoConfiguration注解开启自动配置,加载spring.factories中注册的各种AutoConfiguration类,
当某个AutoConfiguration类满足其注解@Conditional指定的生效条件(Starters提供的依赖、配置或Spring容器中是否存在某个Bean)时,
那么实例化该AutoConfiguration类中定义的Bean(组件等),并注入Spring容器,至此就完成了依赖框架的自动配置。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:完成自动配置开启,扫描各个jar包下的spring.factories文件,并加载文件中注册的AutoConfiguration
spring.factories配置文件:位于jar包的META-INF目录下,按照指定格式注册了自动配置的AutoConfiguration类
AutoConfiguration自动配置类:代表了SpringBoot中一类以xxAutoConfiguration命名的自动配置类
@Conditional条件注解及其衍生注解:在AutoConfiguration类上使用,当满足该条件注解时才会实例化AutoConfiguration类
starters三方组件的依赖及配置:SpringBoot已经预置的组件,SpringBoot默认的starters项目往往只包含了一个pom依赖的项目
03.SpringBoot启动流程
springboot中只需要有@SpringBootApplication这个注解,有了它马上就能够让整个应用跑起来。实际上它只是一个组合注解,@Configuration配置类,@ComponentScan类,包扫描,@EnableAutoConfiguration根据需求自动加载相关的bean这三个注解。
启动流程如下:
1.初始化监听器,以及添加到SpringApplication的自定义监听器。
2.发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件,如果想监听ApplicationStartedEvent事件,你可以这样定义:public class ApplicationStartedListener implements ApplicationListener,然后通过SpringApplication.addListener(..)添加进去即可。
3.装配参数和环境,确定是web环境还是非web环境。
4.装配完环境后,就触发ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件。
5.如果SpringApplication的showBanner属性被设置为true,则打印启动的Banner。
6.创建ApplicationContext,会根据是否是web环境,来决定创建什么类型的ApplicationContext。
7.装配Context的环境变量,注册Initializers、beanNameGenerator等。
8.发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件。
9.注册springApplicationArguments、springBootBanner,加载资源等
10.遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()方法。
11.调用ApplicationContext的refresh()方法,装配context beanfactory等非常重要的核心组件。
12.查找当前ApplicationContext中是否注册有CommandLineRunner,如果有,则遍历执行它们。
13.发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件,启动完毕,表示服务已经可以开始正常提供服务了。通常我们这里会监听这个事件来打印一些监控性质的日志,表示应用正常启动了。
SpringApplication是springboot的入口,启动原理可以重点看下SpringApplication详解(run执行启动)
1.4 配置文件
01.配置文件
a.SpringBoot配置加载顺序:
properties文件 -> YAML文件 -> 系统环境变量 -> 命令行参数 - XML配置(推荐JAVA配置,可以使用 @ImportResource 引入XML配置)
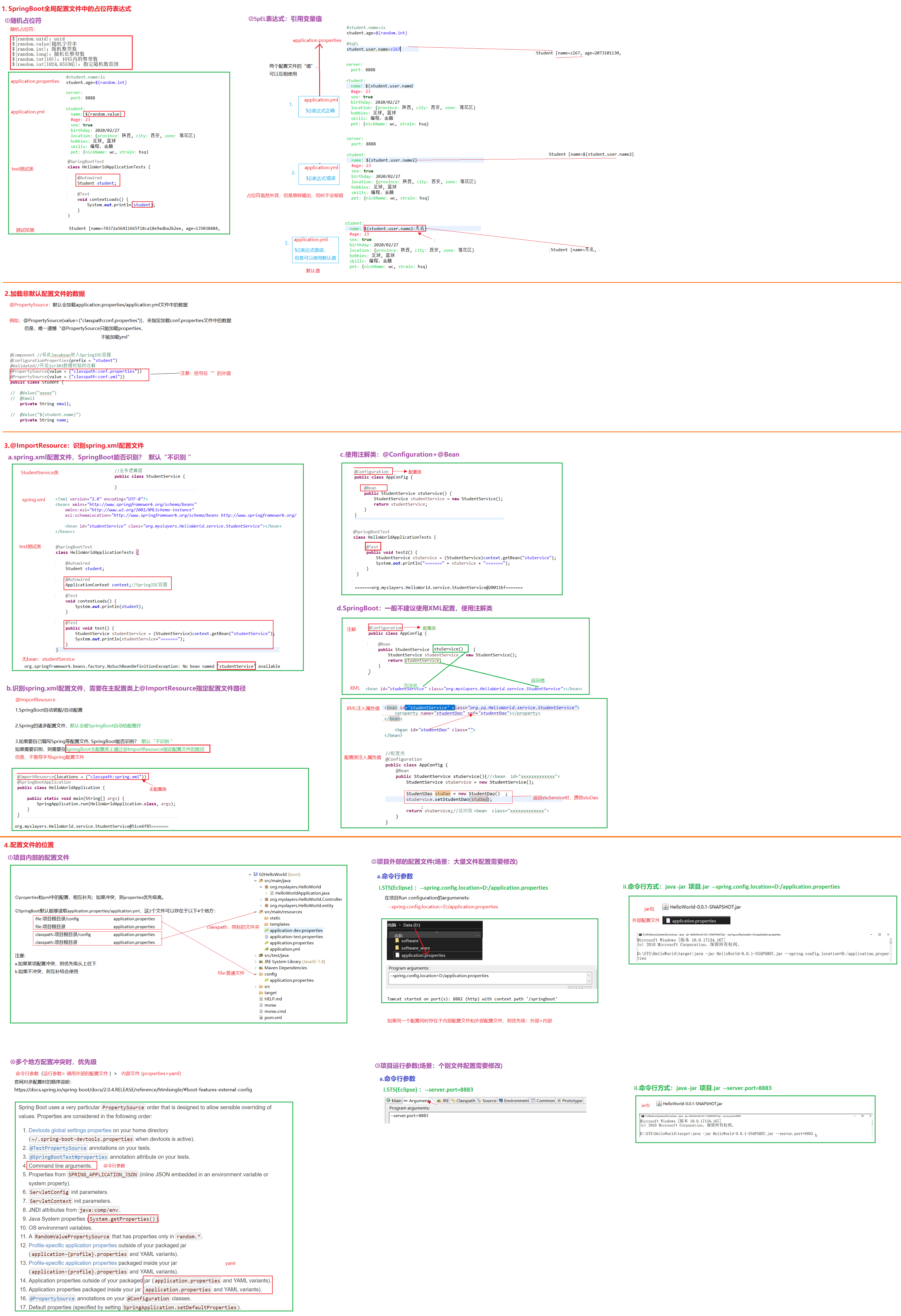
b.SpEL表达式:引用变量值
a.application.properties添加信息
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot_h
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123
b.配置数据源
@Configuration
public class JdbcConfiguration {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
String driverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}
02.@PropertySource:加载非默认配置文件的数据
@PropertySource:默认会加载application.properties / application.yml文件中的数据
例如,@PropertySource(value=('classpath:conf.properties'"),来指定加载conf.properties文件中的数据
但是,唯一遗憾“@PropertySource.只能加载properties,不能加载yml”
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@PropertySource(value {"classpath:conf.properties"})
@PropertySource(value ={"classpath:conf.yml"})
public class Student {
...
}
03.@ImportResource:识别spring.xml配置文件
@ImportResource(locations {"classpath:spring.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldApplication.class, args);
}
}
1.5 多环境切换
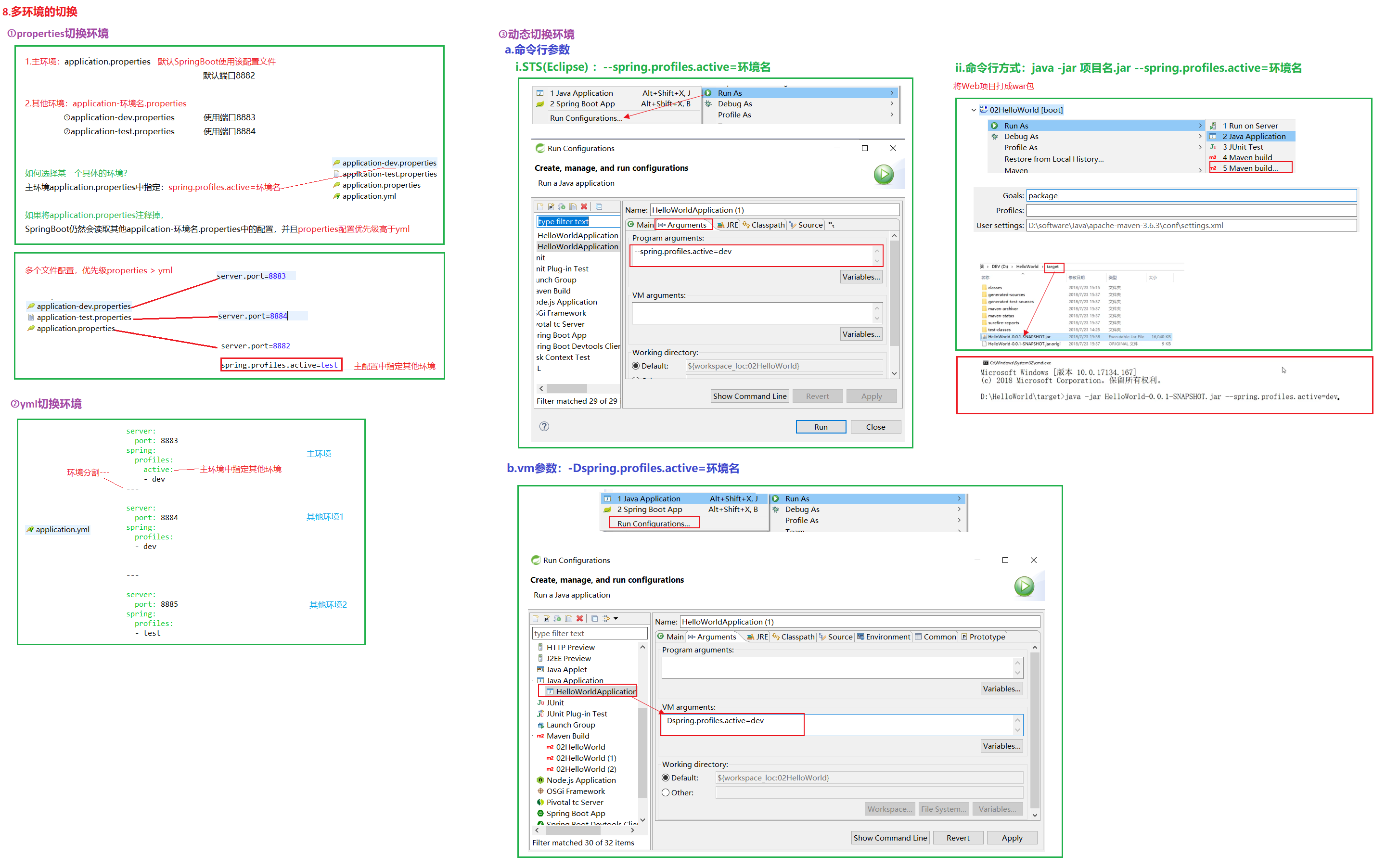
01.propertiest切换环境
spring.profiles.active=dev
02.yml切换环境
spring:
profiles:
active:
- dev
1.6 批量注值、单个注值
01.SpringBoot配置加载顺序:
properties文件 -> YAML文件 -> 系统环境变量 -> 命令行参数 - XML配置(推荐JAVA配置,可以使用 @ImportResource 引入XML配置)
02.@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")与@value:二者可以互补使用
@ConfigurationProperties:同时绑定properties和yml方式的注值,支持批量注值
@value:支持单个注值
03.@ConfigurationProperties批量注值
a.application.yml
student:
name:zs
age:23
sex:true
birthday:2020/02/26
location: {province:"陕ln西",city:'西\n安',zone:莲花n区
hobbies:
-足球
-篮球
skills:
-编程
-金融
pet:
-nickName:wc
-strain:hsq
b.Student.java
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix "student")
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean sex;
private Date birthday;
private Map<String,Object>location;
private String[] hobbies;
private List<String> skills;
private Pet pet;
}
04.@Value单个注值
a.引入数据源连接依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.drtrang</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot2-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
b.application.properties添加信息
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot_h
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123
c.配置数据源
@Configuration
public class JdbcConfiguration {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
String driverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}
05.6种方式读取Springboot的配置
a.Environment
只要注入Environment类调用其方法getProperty(属性key)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class EnvironmentTest {
@Resource
private Environment env;
@Test
public void var1Test() {
String var1 = env.getProperty("env101.var1");
log.info("Environment 配置获取 {}", var1);
}
}
b.@Value
@Value注解是Spring框架提供的用于注入配置属性值的注解,它可用于类的成员变量、方法参数和构造函数参数上。
在应用程序启动时,使用 @Value 注解的 Bean 会被实例化。所有使用了 @Value 注解的 Bean 会被加入到 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 的后置处理器集合中。
当后置处理器开始执行时,它会读取 Bean 中所有 @Value 注解所标注的值,并通过反射将解析后的属性值赋值给标有 @Value 注解的成员变量、方法参数和构造函数参数。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class EnvVariablesTest {
@Value("${env101.var1}")
private String var1;
@Test
public void var1Test(){
log.info("配置文件属性: {}",var1);
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.缺失配置
如果在代码中引用变量,配置文件中未进行配值,就会出现类似下图所示的错误:
Could not resolve placeholder 'env101.var1'in value "${env101.var1}"
为了避免此类错误导致服务启动异常,我们可以在引用变量的同时给它赋一个默认值,以确保即使在未正确配值的情况下,程序依然能够正常运行。
@Value("${env101.var1:我是小富}")
private String var1;
2.静态变量(static)赋值
还有一种常见的使用误区,就是将 @Value 注解加到静态变量上,这样做是无法获取属性值的。
静态变量是类的属性,并不属于对象的属性,而 Spring是基于对象的属性进行依赖注入的,类在应用启动时静态变量就被初始化,
此时 Bean还未被实例化,因此不可能通过 @Value 注入属性值。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
即使 @Value 注解无法直接用在静态变量上,我们仍然可以通过获取已有 Bean实例化后的属性值,再将其赋值给静态变量来实现给静态变量赋值。
我们可以先通过 @Value 注解将属性值注入到普通 Bean中,然后在获取该 Bean对应的属性值,并将其赋值给静态变量。这样,就可以在静态变量中使用该属性值了。
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class EnvVariablesTest {
private static String var3;
private static String var4;
@Value("${env101.var3}")
public void setVar3(String var3) {
var3 = var3;
}
EnvVariablesTest(@Value("${env101.var4}") String var4){
var4 = var4;
}
public static String getVar4() {
return var4;
}
public static String getVar3() {
return var3;
}
}
3.常量(final)赋值
@Value 注解加到final关键字上同样也无法获取属性值,因为 final 变量必须在构造方法中进行初始化,
并且一旦被赋值便不能再次更改。而 @Value 注解是在 bean 实例化之后才进行属性注入的,
因此无法在构造方法中初始化 final 变量。
4.非注册的类中使用
只有标注了@Component、@Service、@Controller、@Repository 或 @Configuration 等容器管理注解的类,
由 Spring 管理的 bean 中使用 @Value注解才会生效。
而对于普通的POJO类,则无法使用 @Value注解进行属性注入。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @value注解 非注册的类中使用
* `@Component`、`@Service`、`@Controller`、`@Repository` 或 `@Configuration` 等
* 容器管理注解的类中使用 @Value注解才会生效
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TestService {
@Value("${env101.var7}")
private String var7;
public String getVar7(){
return this.var7;
}
}
5.引用方式不对
如果我们想要获取 TestService 类中的某个变量的属性值,需要使用依赖注入的方式,而不能使用 new 的方式。
通过依赖注入的方式创建 TestService 对象,Spring 会在创建对象时将对象所需的属性值注入到其中。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @value注解 引用方式不对
*/
@Test
public void var7_1Test() {
TestService testService = new TestService();
log.info("引用方式不对 注入: {}", testService.getVar7());
}
c.@ConfigurationProperties
application.yml
env101:
var1: var1-公众号:程序员小富
var2: var2-公众号:程序员小富
创建一个 MyConf 类用于承载所有前缀为env101的配置属性。
@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "env101")
public class MyConf {
private String var1;
private String var2;
}
在需要使用var1、var2属性值的地方,将 MyConf 对象注入到依赖对象中即可。
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class ConfTest {
@Resource
private MyConf myConf;
@Test
public void myConfTest() {
log.info("@ConfigurationProperties注解 配置获取 {}", JSON.toJSONString(myConf));
}
}
d.@PropertySources
在 src/main/resources/ 目录下创建自定义配置文件 xiaofu.properties,增加两个属性。
env101.var9=var9-程序员小富
env101.var10=var10-程序员小富
在需要使用自定义配置文件的类上添加 @PropertySources 注解,注解 value属性中指定自定义配置文件的路径,可以指定多个路径,用逗号隔开。
@Data
@Configuration
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:xiaofu.properties",encoding = "utf-8"),
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:xiaofu.properties",encoding = "utf-8")
})
public class PropertySourcesConf {
@Value("${env101.var10}")
private String var10;
@Value("${env101.var9}")
private String var9;
}
e.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean 加载 YAML 文件
略
f.自定义读取
略
1.7 日志
01.SpringBoot默认选用slf4j,logback
02.日志级别:TRACE<DEBUG<INFO<WARN<ERROR<FATAL<OFF
03.SpringBoot默认日志级别:info(只打印info及之后级别的信息)
04.自定义日志级别:logging.level..org.myslayers.HelloWorld=warn
2 SpringBoot基本配置
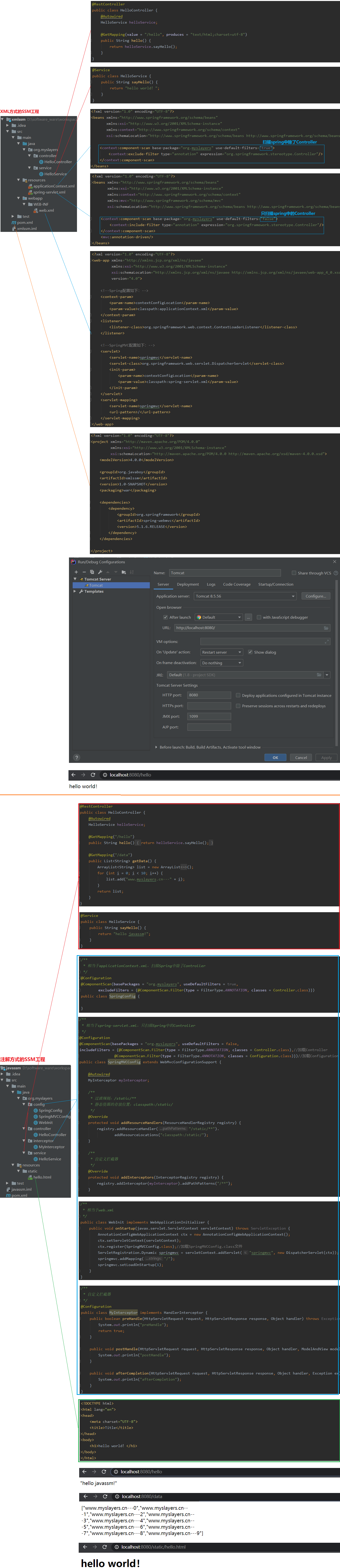
2.1 SSM工程
2.2 Web容器
01.SpringBoot添加了spring-boot-starter-web依赖后,默认会使用Tomcat作为Web容器(无需添加依赖),如果需要对Tomcat做进一步配置,可以在application.properties中配置
server.port=8001 --端口号
server.error.path=/error --项目出错时跳转的页面
server.servlet.session.timeout=30m --session失效时间:30m代表30分钟,以秒为单位
server.servlet.context-path=/chapter02 --项目名称,默认为"/"
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=utf-8 --Tomcat请求编码
server.tomcat.max-threads=5OO --Tomcat最大线程数
server.tomcat.basedir=/home/sang/tmp --basedir表示存放Tomcat运行日志和临时文件的目录
02.加入Jetty依赖(从spring-boot-starter-web除去默认Tomcat),然后启动项目,查看启动日志
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot- starter-web</artifactid>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artif actid>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactid>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactid>
</dependency>
03.加入Undertow依赖(从spring-boot-starter-web除去默认Tomcat),然后启动项目,查看启动日志
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot- starter-web</artifactid>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artif actid>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactid>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactid>
</dependency>
2.3 全局配置文件
01.application.properties(文件的4个位置):项目根目录下的config文件夹、项目根目录下、classpath下的config文件夹、项目根目录下
a.给对象注值(简单类型)
student.name=ls
student.age=23
b.绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") + @Component
02.application.yml(引入spring-boot-starter-web会间接地引入snakeyaml依赖来解析YAML)
a.给对象注值(简单类型、Map类型、集合/数组、对象)(Set/List/数组 []可省、 Map/对象 {}不可省)
student:
name: zs
age: 23
birthday: 2020/02/26
location: {province: 陕西, city: 西安, zone: 莲花区}
hobbies: 足球, 篮球
skills: 编程, 金融
pet: {nickName: wc, strain: hsq}
b.绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") + @Component
3 SpringBoot整合视图层技术
3.1 Thymeleaf
01.示例
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
3.2 FreeMarker
01.示例
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.freemarker")
public class FreeMarkerProperties extends AbstractTemplateViewResolverProperties {
public static final String DEFAULT_TEMPLATE_LOADER_PATH = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".ftl";
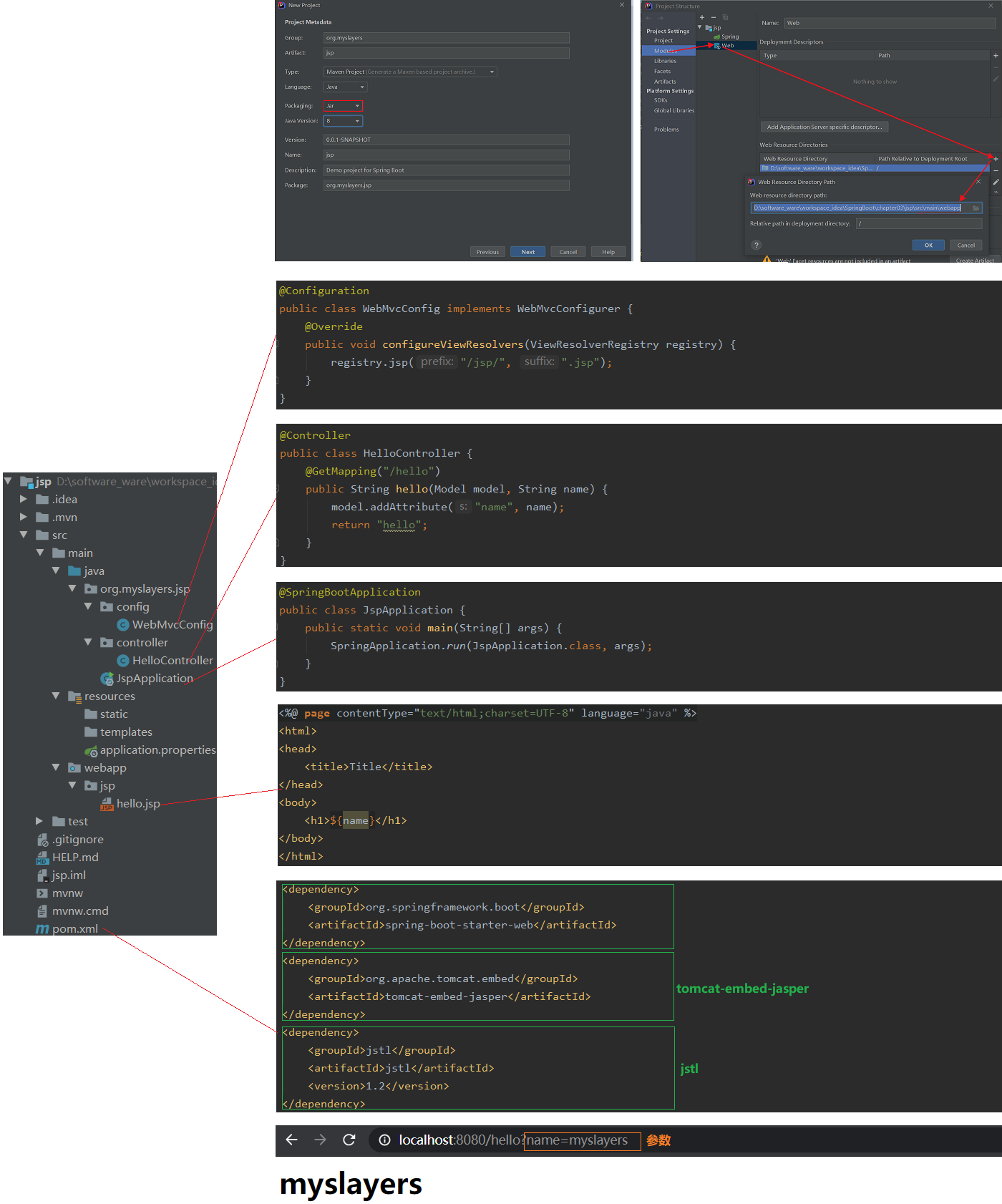
3.3 Jsp
4 SpringBoot整合Web开发
4.1 返回JSON数据
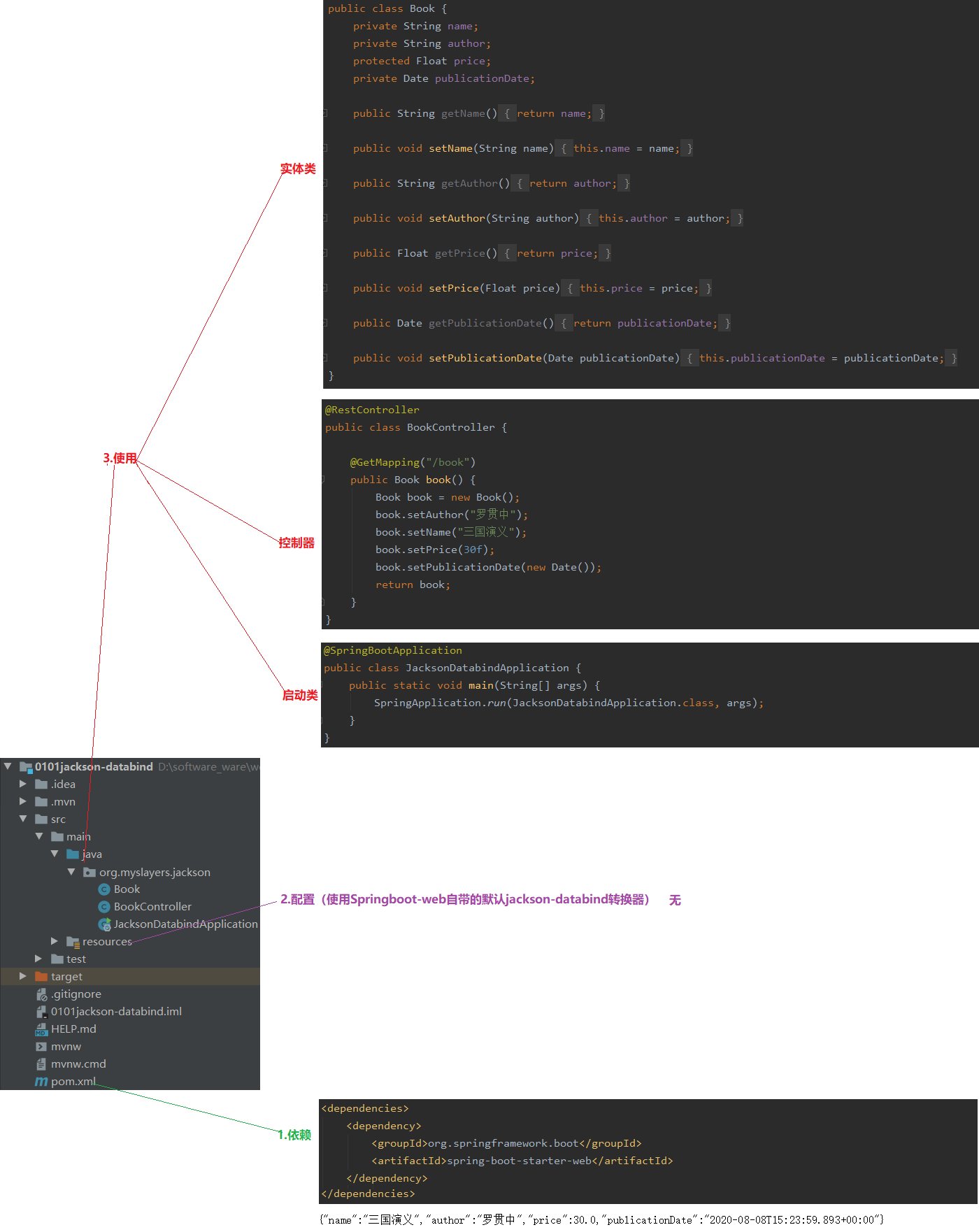
4.1.1 jackson-databind
01.介绍
spring-boot-starter-web中默认加入了jackson-databind作为JSON处理器
默认使用HttpMessageConverter接口实现类中的MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter类型转换器
02.HttpMessageConverter接口,共有5个方法
a.获取支持的MediaType(application/json之类)
b.接收到请求时判断是否能读(canRead)
c.能读则读(read)
d.返回结果时判断是否能写(canWrite)
e.能写则写(write)
4.1.2 Gson
01.介绍
由于Spring Boot中默认提供了Gson的自动转换类GsonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration
因此Gson的依赖添加成功后,可以像使用jackson-databind那样直接使用Gson
但是在Gson进行转换时,如果想对日期数据进行格式化,那么还需要开发者自定义HttpMessageConverter
02.源码解读:@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解表示当项目中没有提供GsonHttpMessageConverter时才会使用默认的类型转换器
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnBean({Gson.class}) @Conditional({GsonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration.PreferGsonOrJacksonAndJsonbUnavailableCondition.class})
static class GsonHttpMessageConverterConfiguration {
GsonHttpMessageConverterConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean//默认的类型转换器
GsonHttpMessageConverter gsonHttpMessageConverter(Gson gson) {
GsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new GsonHttpMessageConverter();
converter.setGson(gson);
return converter;
}
}
03.配置类:自定义类型转换器
@Configuration
public class GsonConfig {
@Bean
GsonHttpMessageConverter gsonHttpMessageConverter() {
GsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new GsonHttpMessageConverter();
GsonBuilder builder = new GsonBuilder();
builder.setDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");//设置Gson解析时日期的格式
builder.excludeFieldsWithModifiers(Modifier.PROTECTED);//设置Gson解析时修饰符为protected的字段被过滤掉
Gson gson = builder.create();
converter.setGson(gson);
return converter;
}
}
4.1.3 fastjson
01.介绍
fastjson是阿里巴巴的一个开源JSON解析框架,是目前JSON解析速度最快的开源框架,该框架也可以集成到Spring Boot中
不同于Gson, fastjson继承完成之后并不能立马使用,需要我们自己提供相应的HttpMessageConverter后才能使用
因此,我们通过配置类自定义类型转换器,然后放入Spring容器中
02.配置类:自定义类型转换器
@Configuration
public class MyFastJsonConfig {
@Bean
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastJsonHttpMessageConverter() {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
FastJsonConfig config = new FastJsonConfig();
config.setDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");//日期格式
config.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));//数据编码
config.setSerializerFeatures(
SerializerFeature.WriteClassName,//是否在生成的JSON中输出类名
SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,//是否输出value为null的数据
SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat,//生成的JSON格式化
SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,//空集合输出[],而非null
SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty//空字符串输出"",而非null
);
converter.setFastJsonConfig(config);
return converter;
}
}
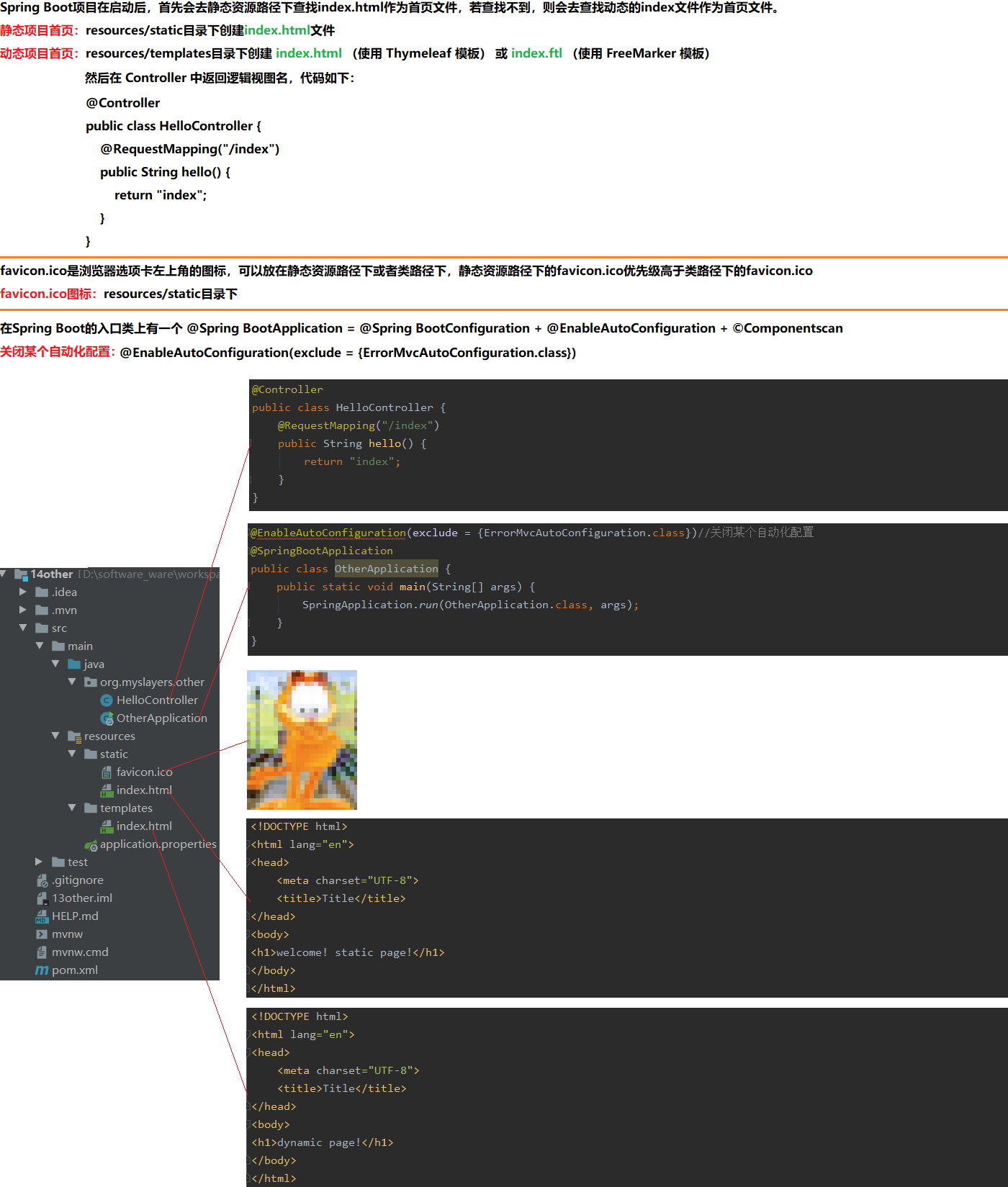
4.2 静态资源访问
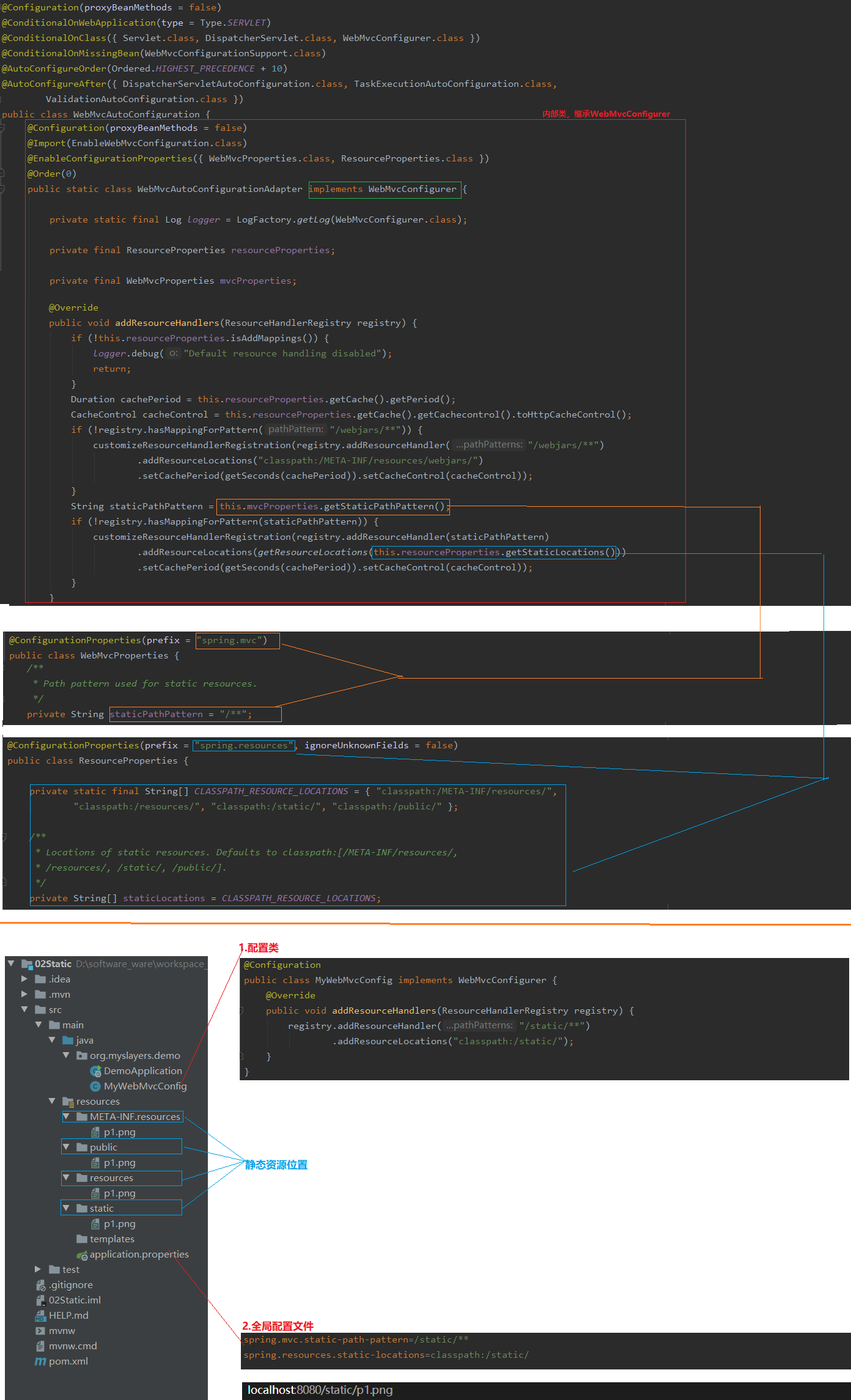
01.SpringBoot中对于SpringMVC的自动化配置都在WebMvcAutoConfiguration类中,它有一个一个静态内部类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter,实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口。WebMvcConfigurer接口中有一个方法addResourceHandlers, 是用来配置静态资源过滤的。
过滤规则(默认):
/**
静态资源的默认5个位置:
classpath:/META-INF/resources/,
classpath:/resources/,
classpath:/static/,
classpath:/public/
/
02.自定义规则
a.application.properties
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/static/
b.配置类
@Configuration
public class MyWebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/static/");
}
}
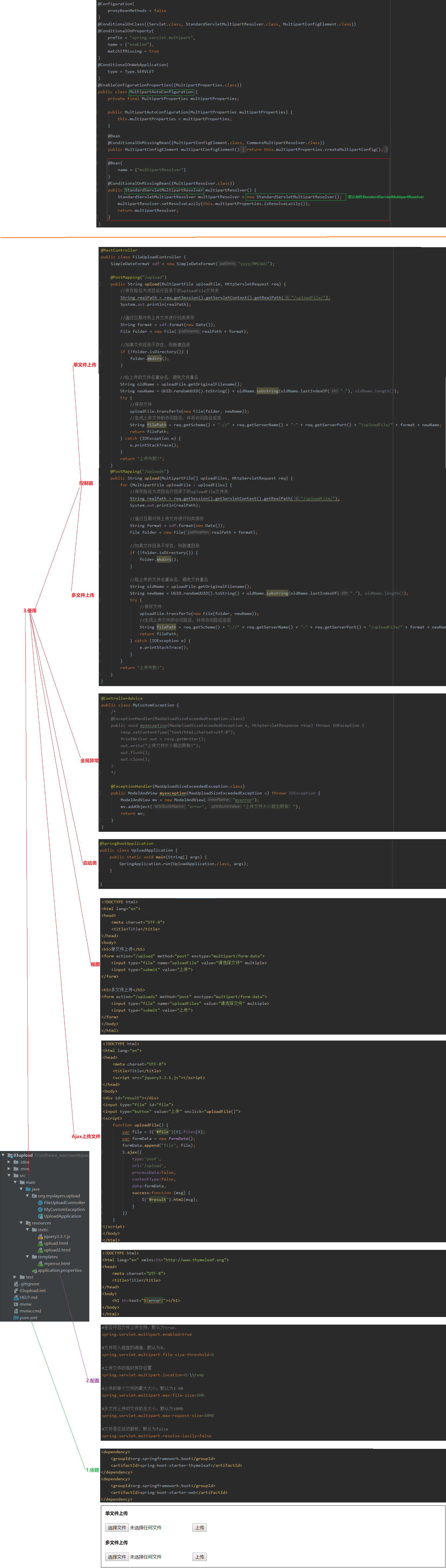
4.3 文件上传
01.Java中的文件上传一共涉及两个组件
CommonsMultipartResolver:使用commons-fileload来处理multipart请求
StandardServletMultipartResolver:基于Servlet3.0来处理multipart请求,SpringBoot2.x内置的Tomcat为8.x版本,因此SpringBoot文件上传自动化配置类MultipartAutoConfiguration,默认使用该组件StandardServletMultipartResolver。如果没有提供MultipartResolver,则使用该默认组件。
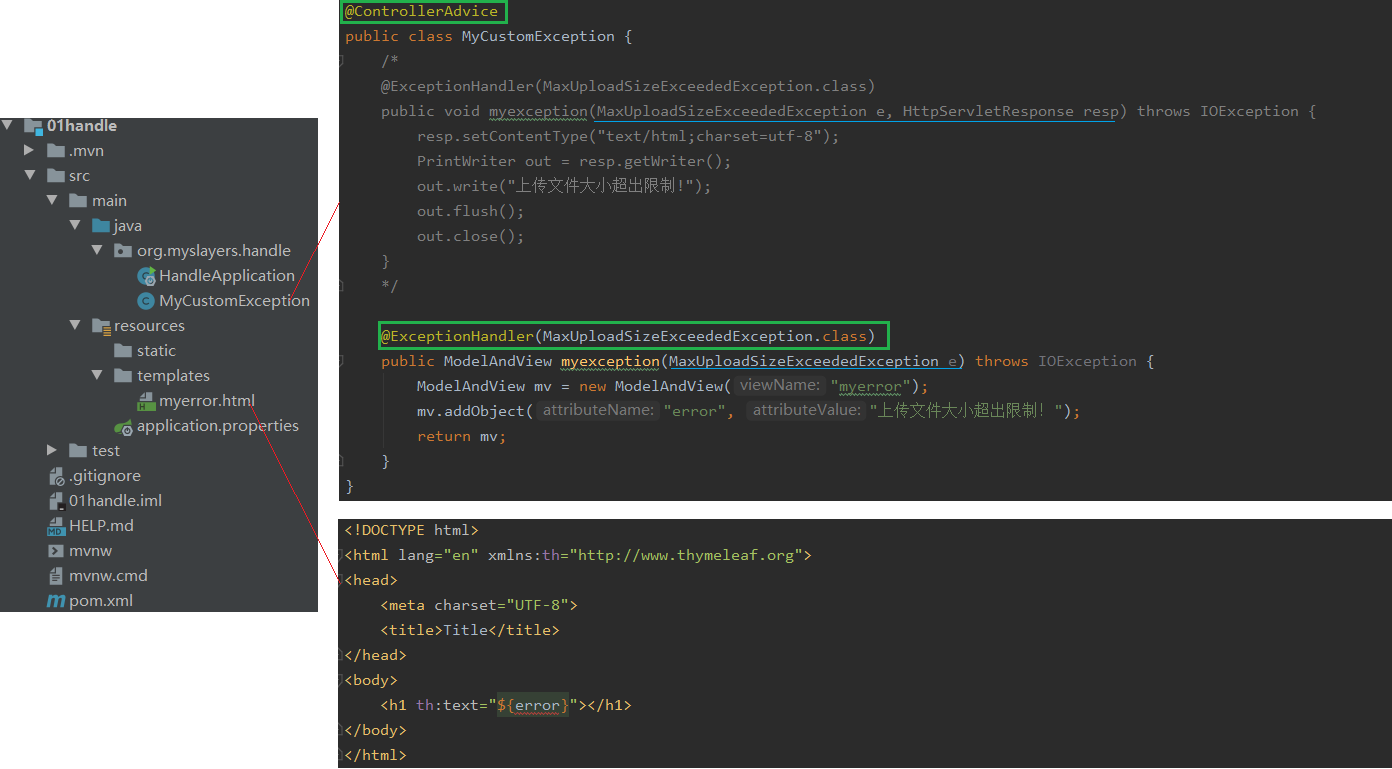
4.4 @ControllerAdvice
4.4.1 全局异常处理
01.@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class):处理所有类型的异常
方法参数:异常实例、HttpServletResponse、HttpServletRequest、Model
方法返回值:JSON、ModelAndView、逻辑视图名
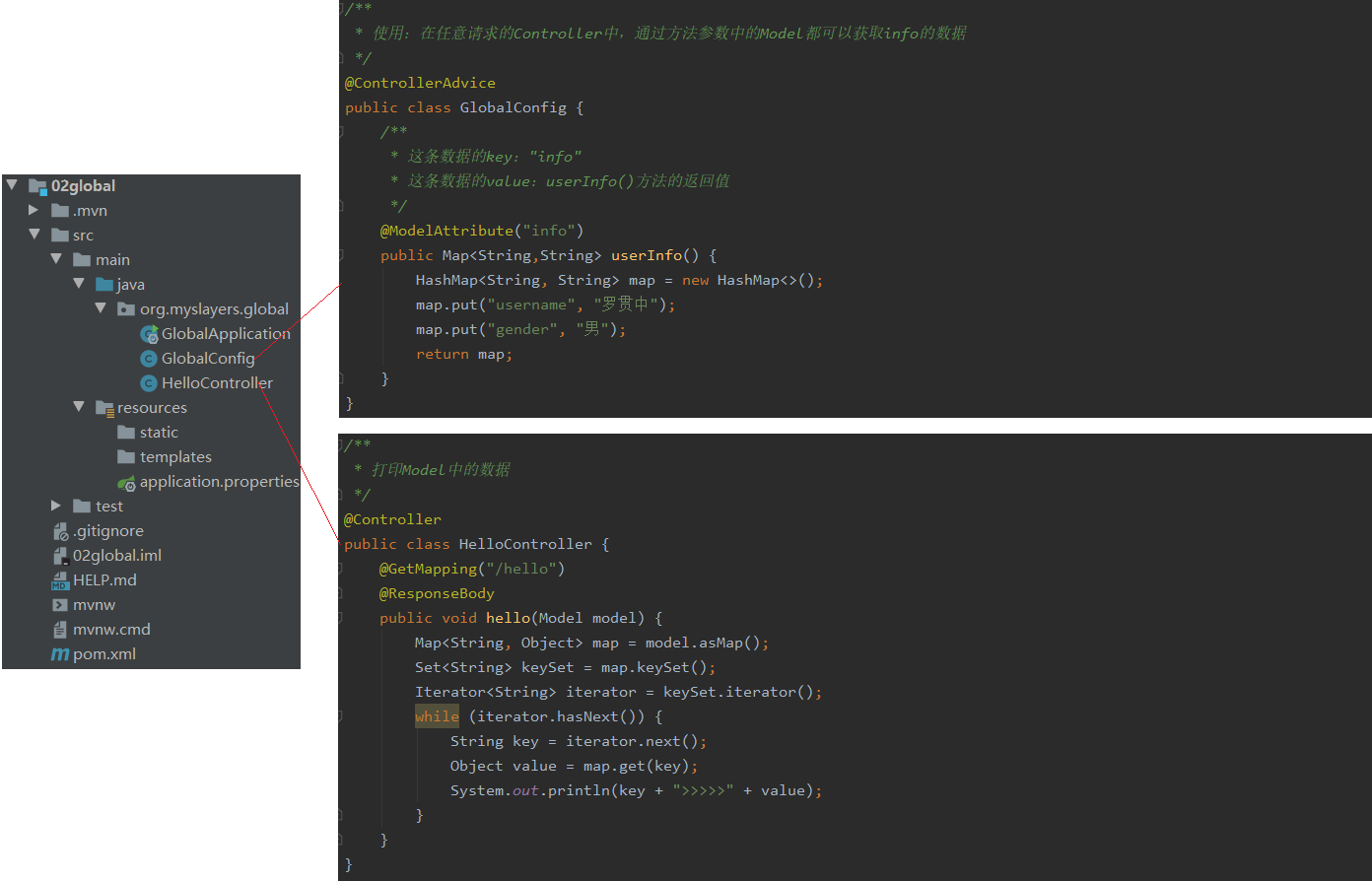
4.4.2 添加全局数据
01.@ControllerAdvice + @ModelAttribute
key:"info"
value:userInfo()方法的返回值
使用:在任意请求的Controller中,通过方法参数中的Model都可以获取info的数据
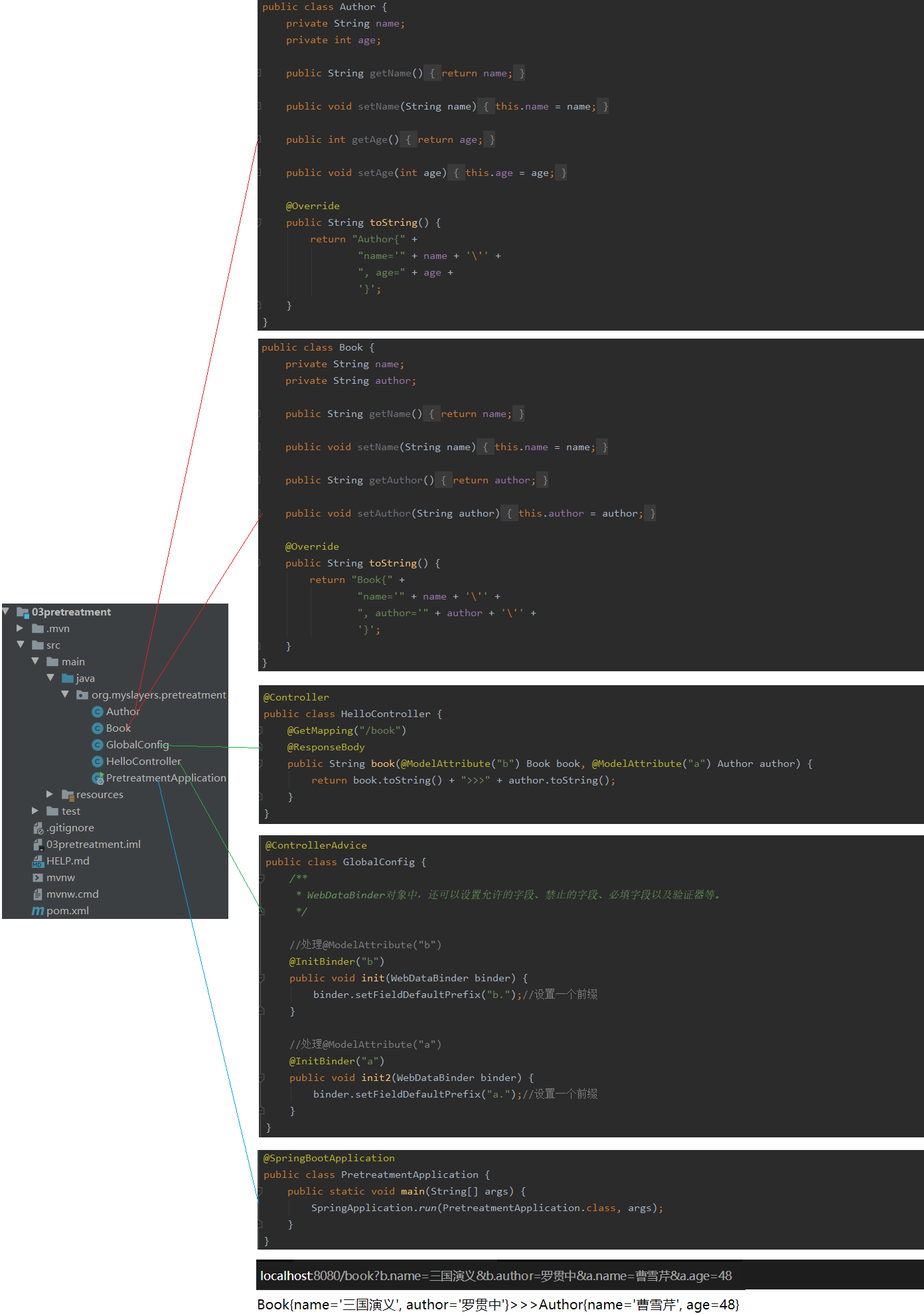
4.4.3 请求参数预处理
01.@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler
将表单中的数据绑定到实体类上时进行一些额外处理,例如解决实体类中name属性混淆问题
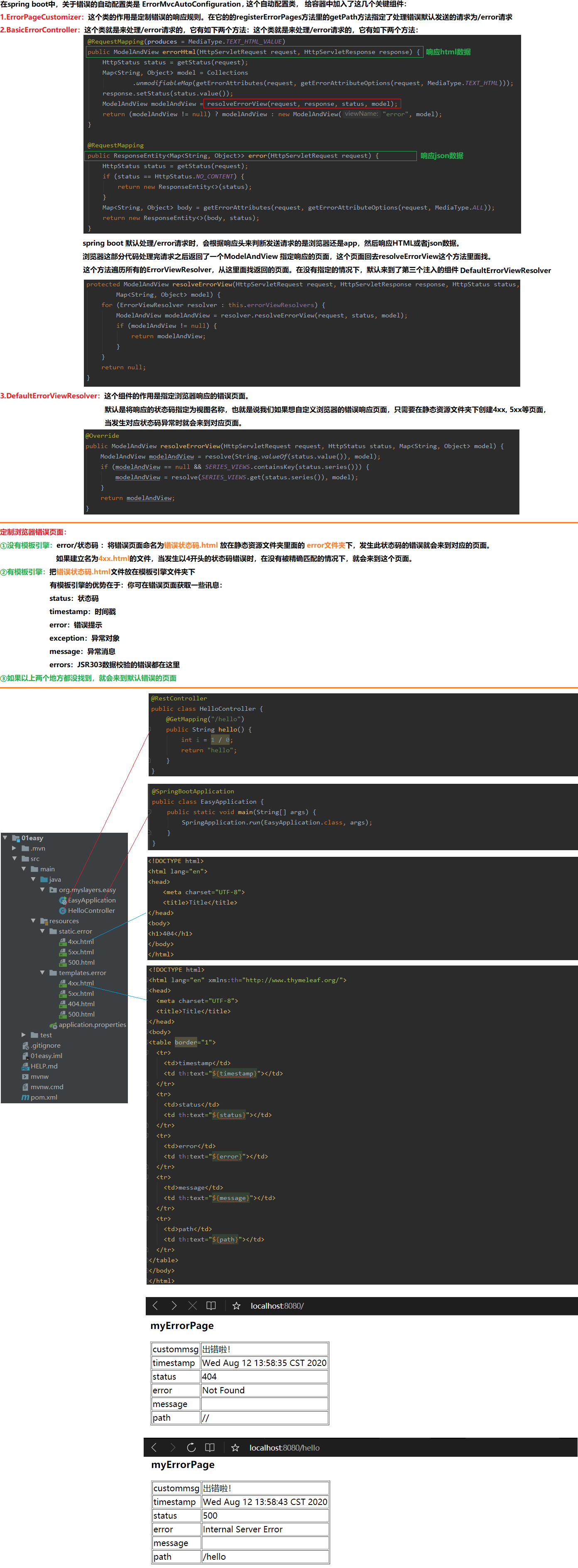
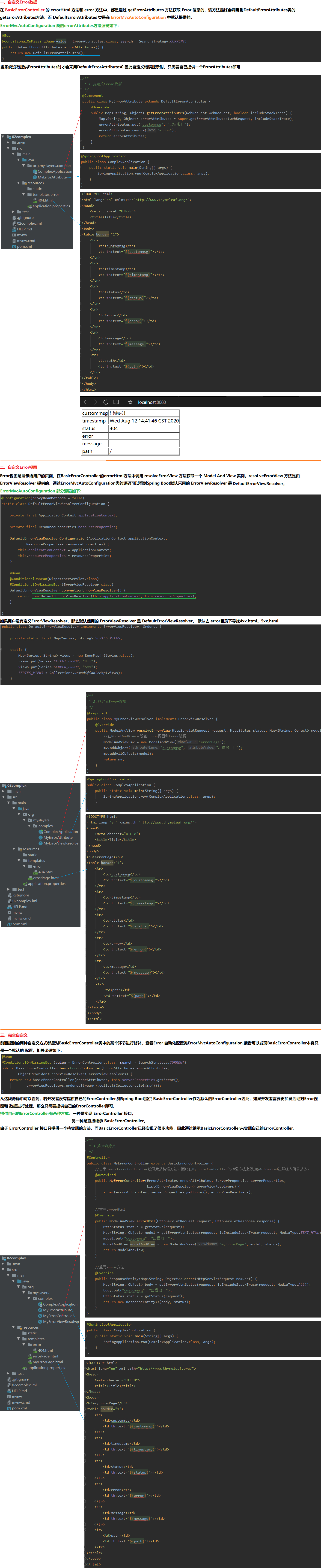
4.5 自定义错误页
4.5.1 简单配置
4.5.2 复杂配置
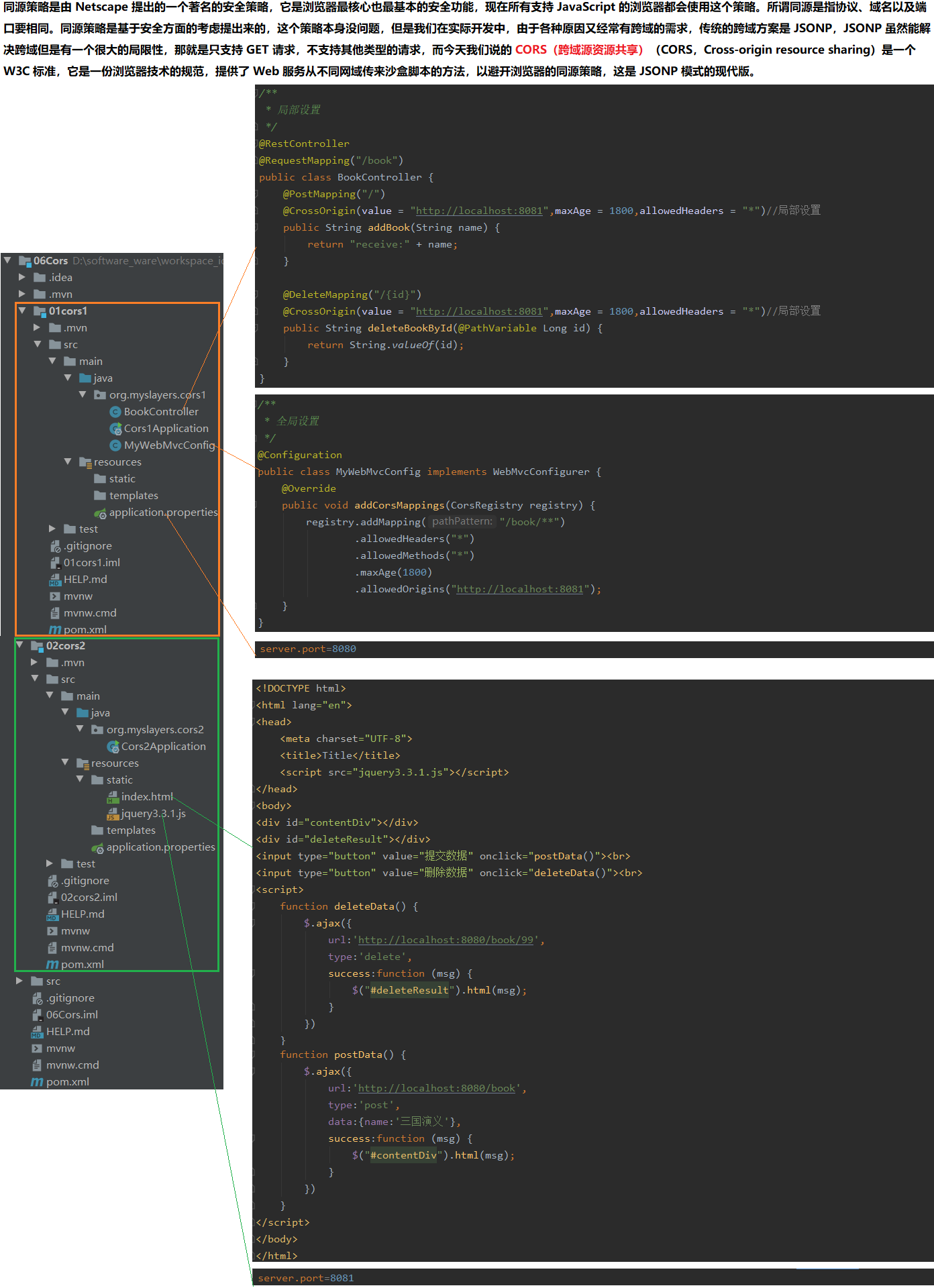
4.6 CORS 支持
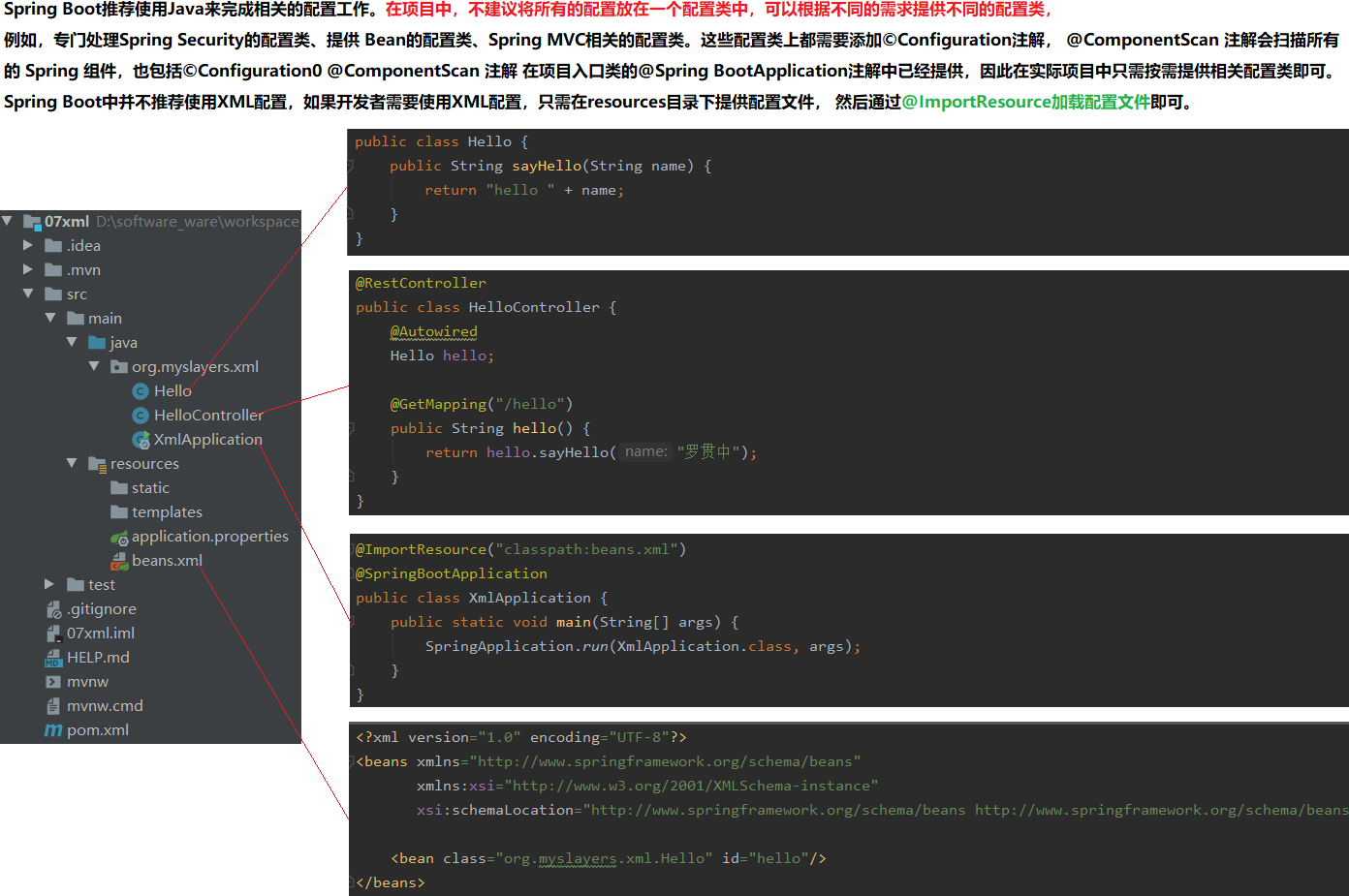
4.7 XML配置
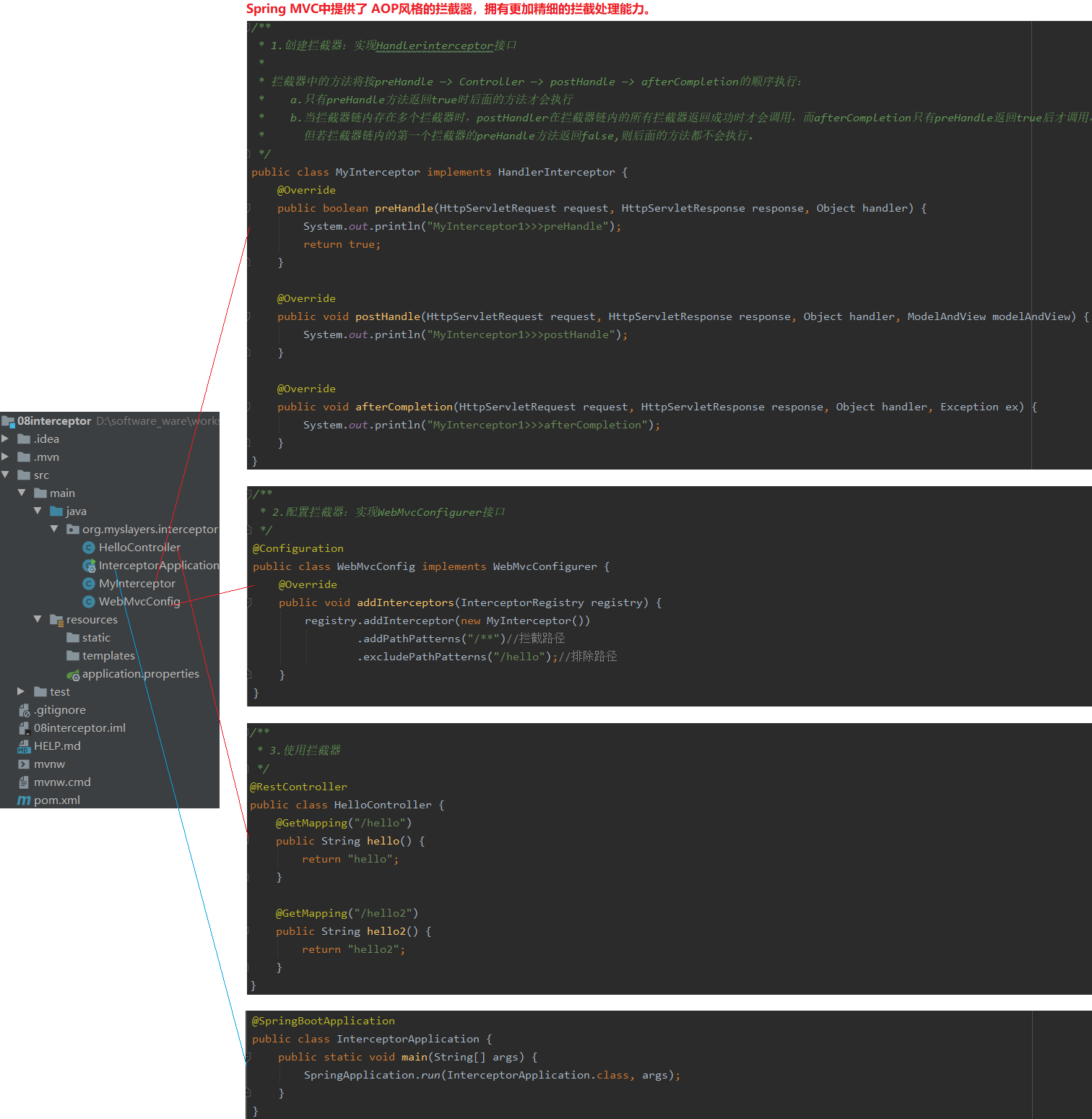
4.8 注册拦截器
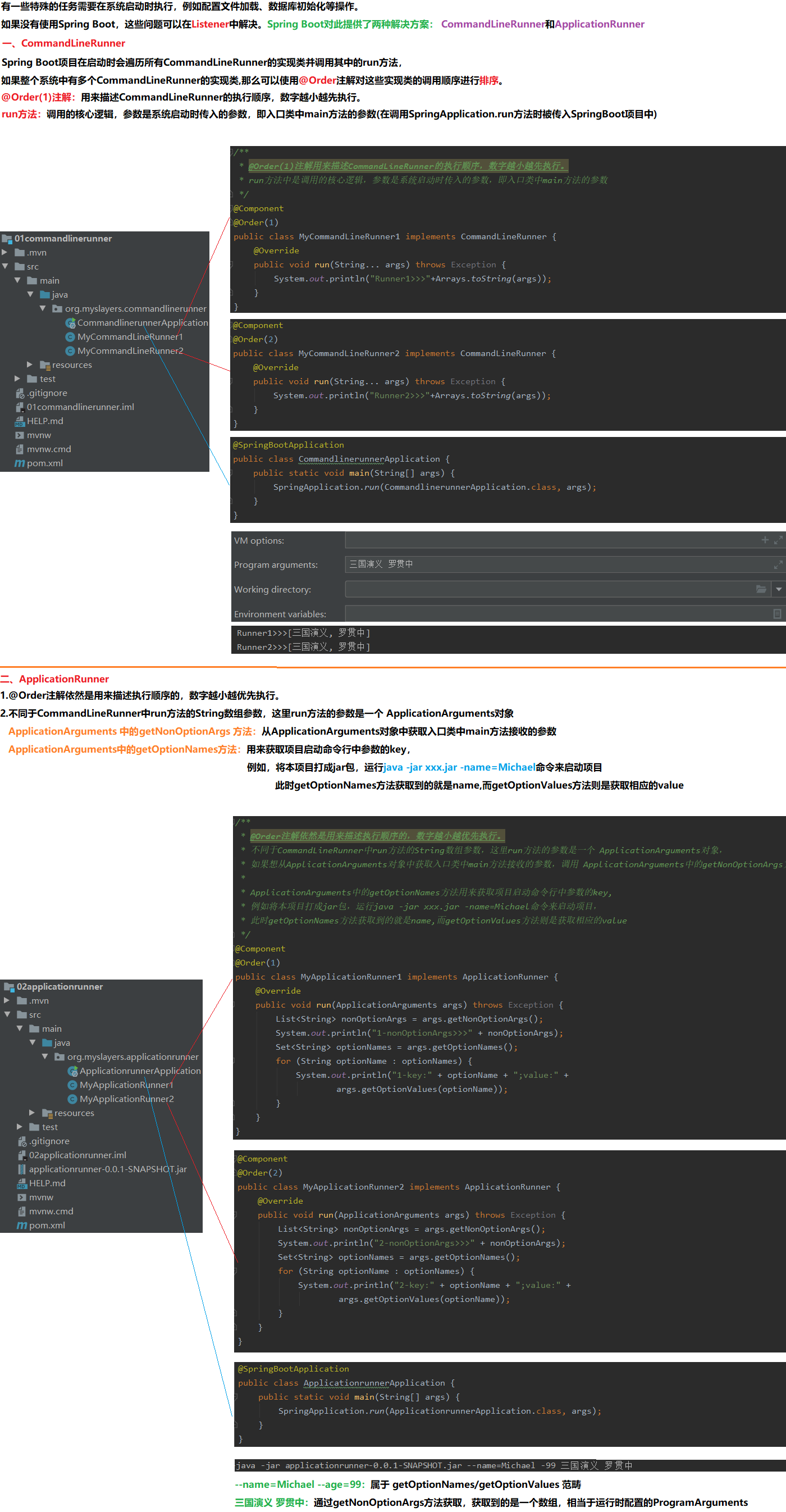
4.9 启动系统任务
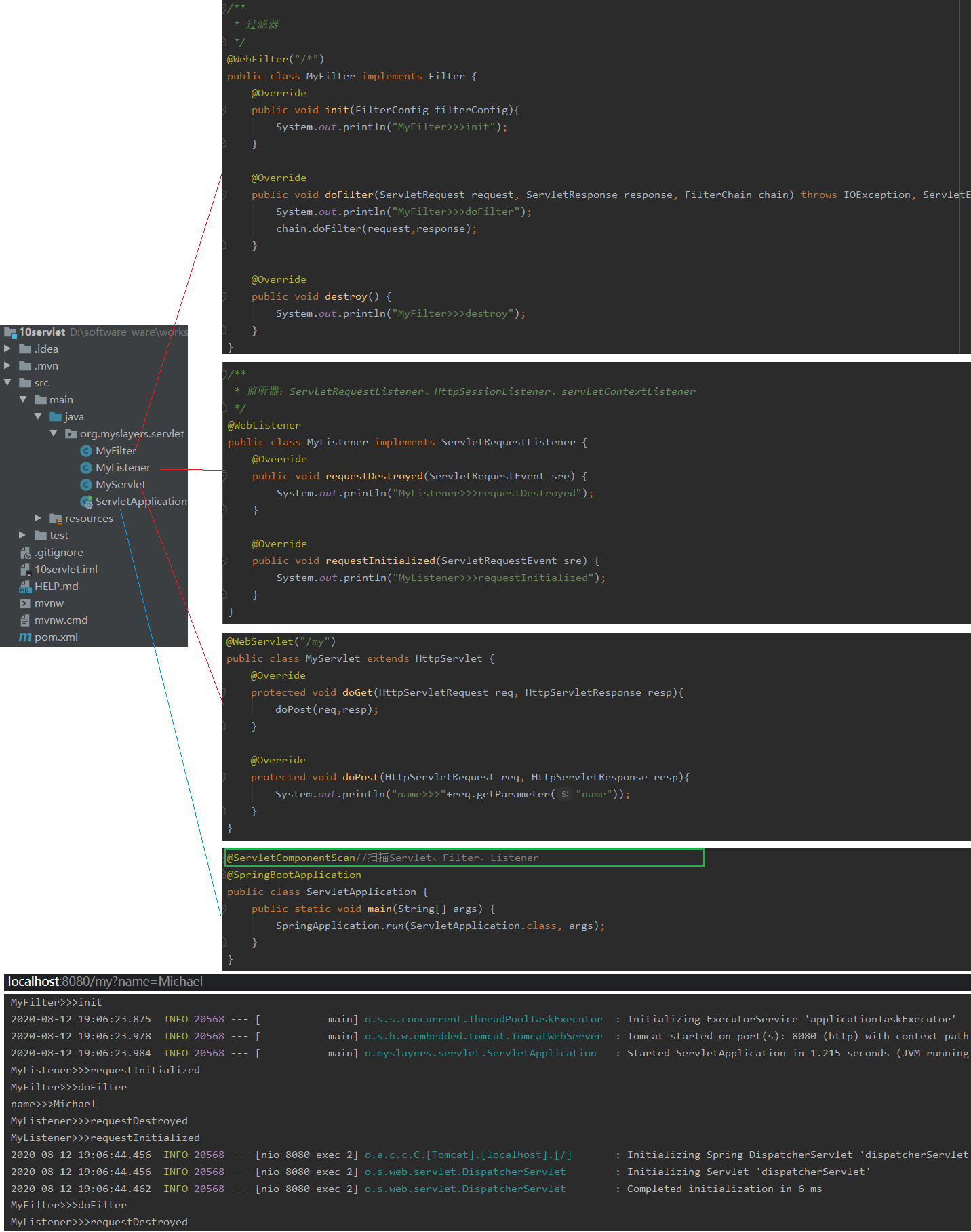
4.10 整合Servlet、Filter、Listener
00.汇总
@WebServlet("/my")
@WebFilter("/*")
@WebListener
@ServletComponentScan:扫描Servlet、Filter、Listener
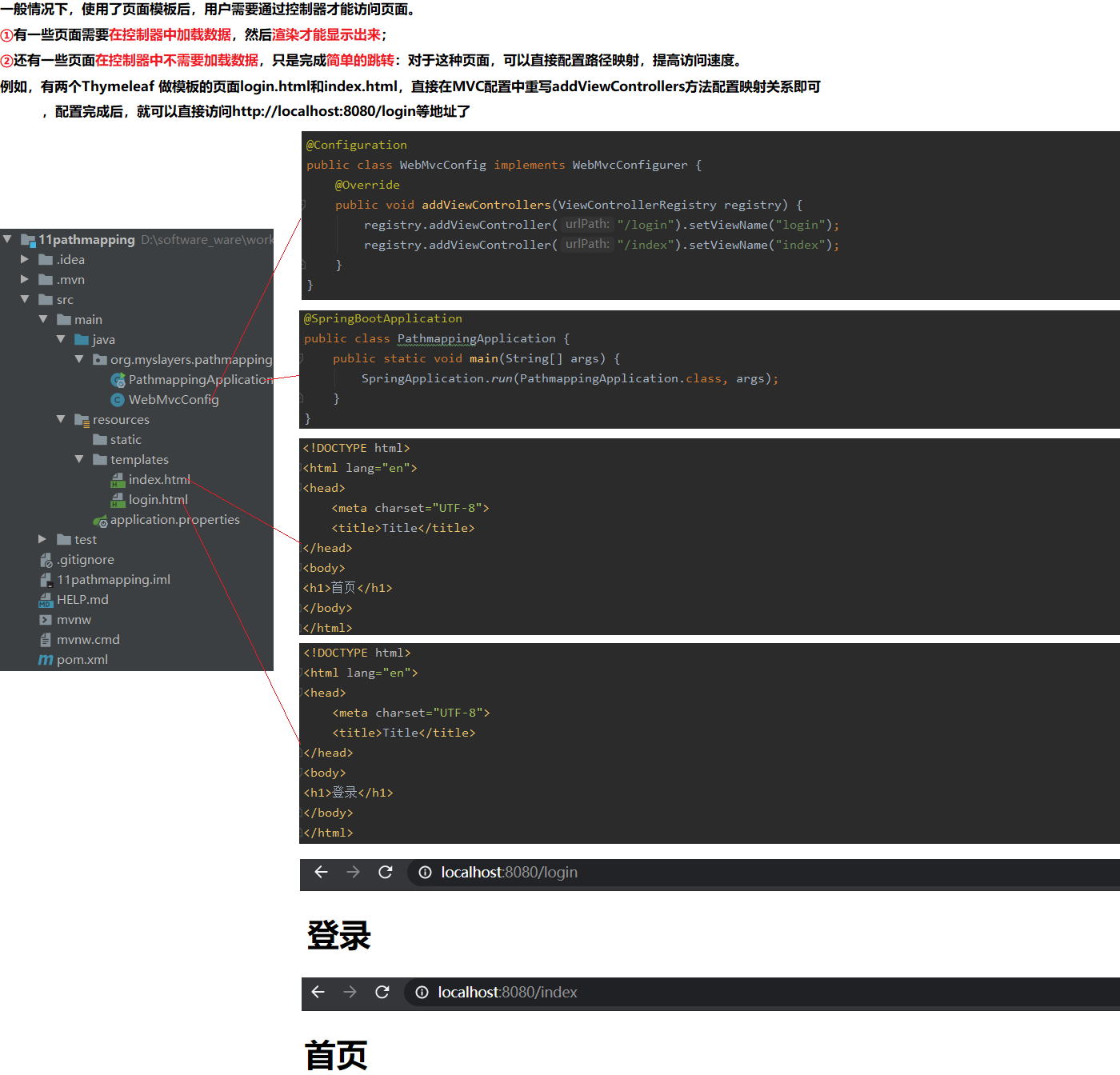
4.11 路径映射
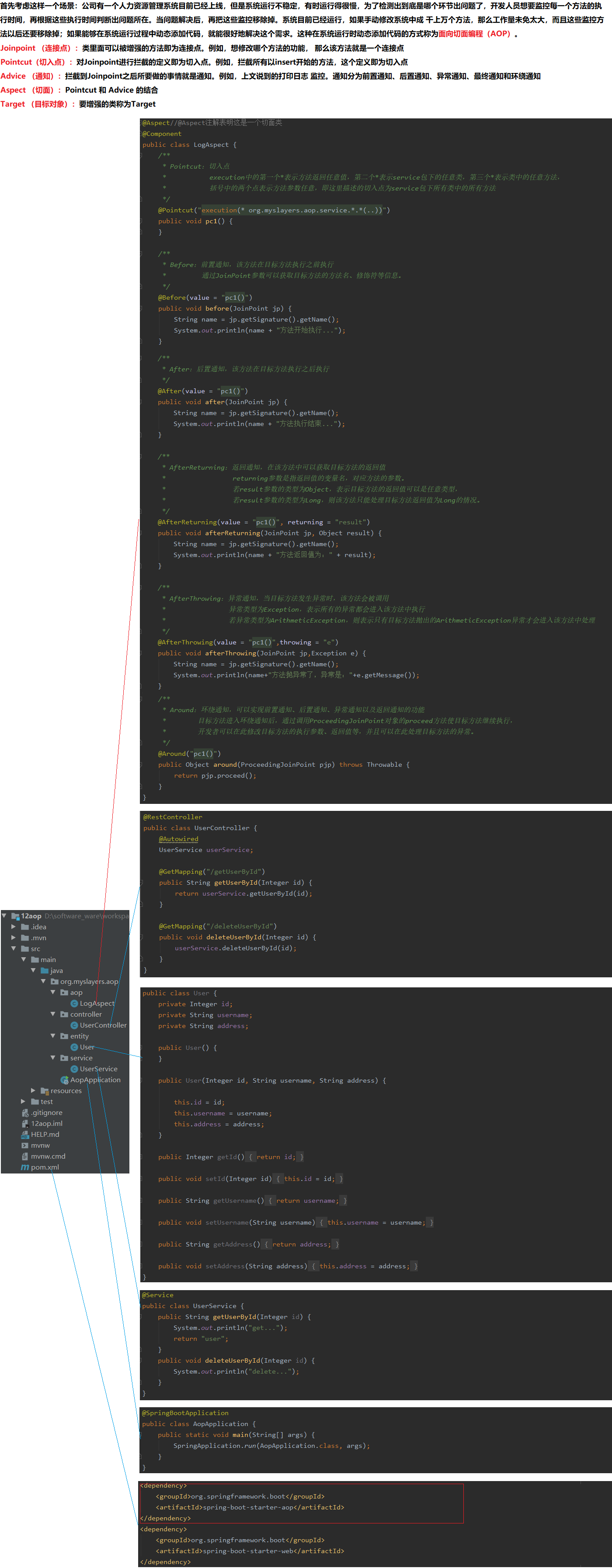
4.12 面向切面编程
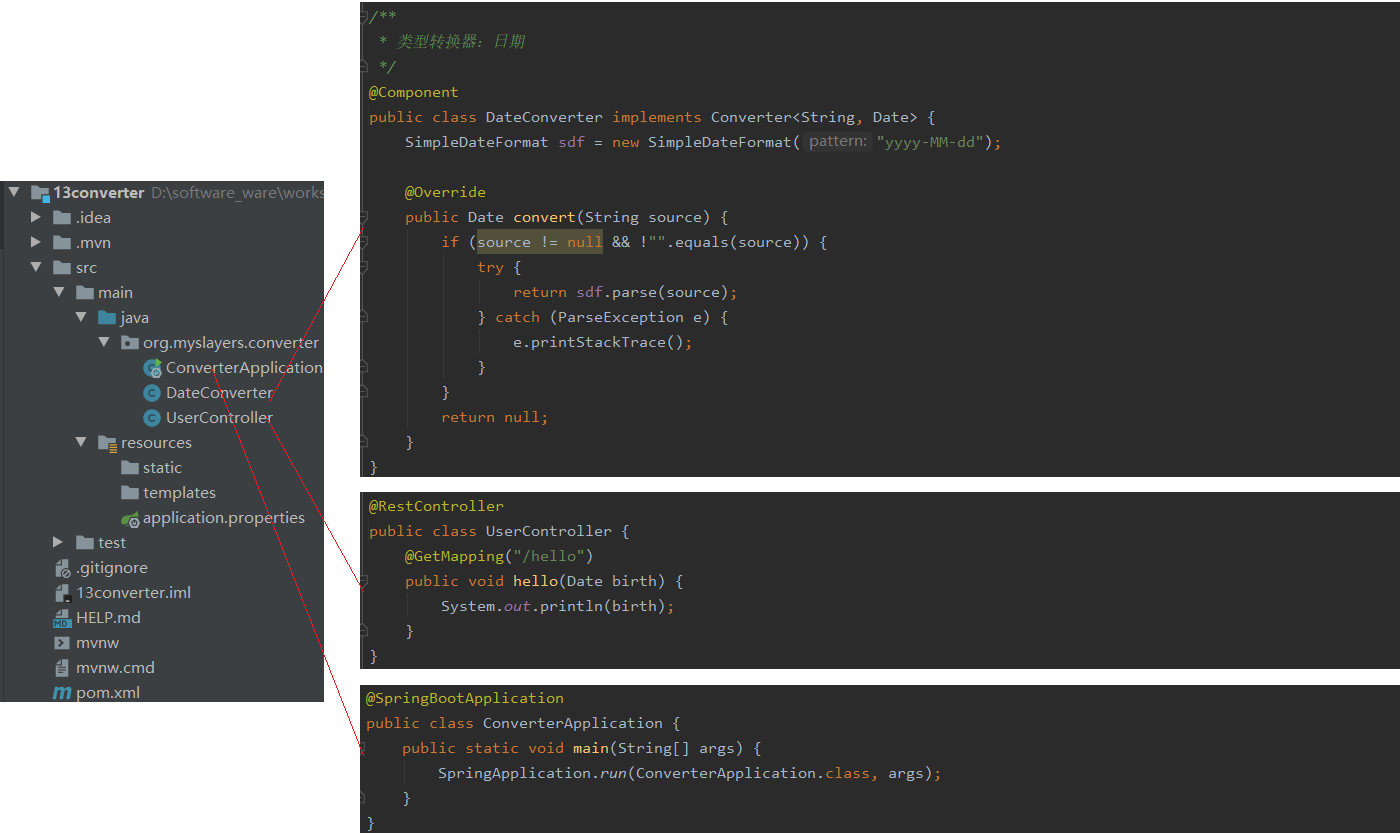
4.13 类型转换器
4.14 其他
5 SpringBoot整合持久层技术
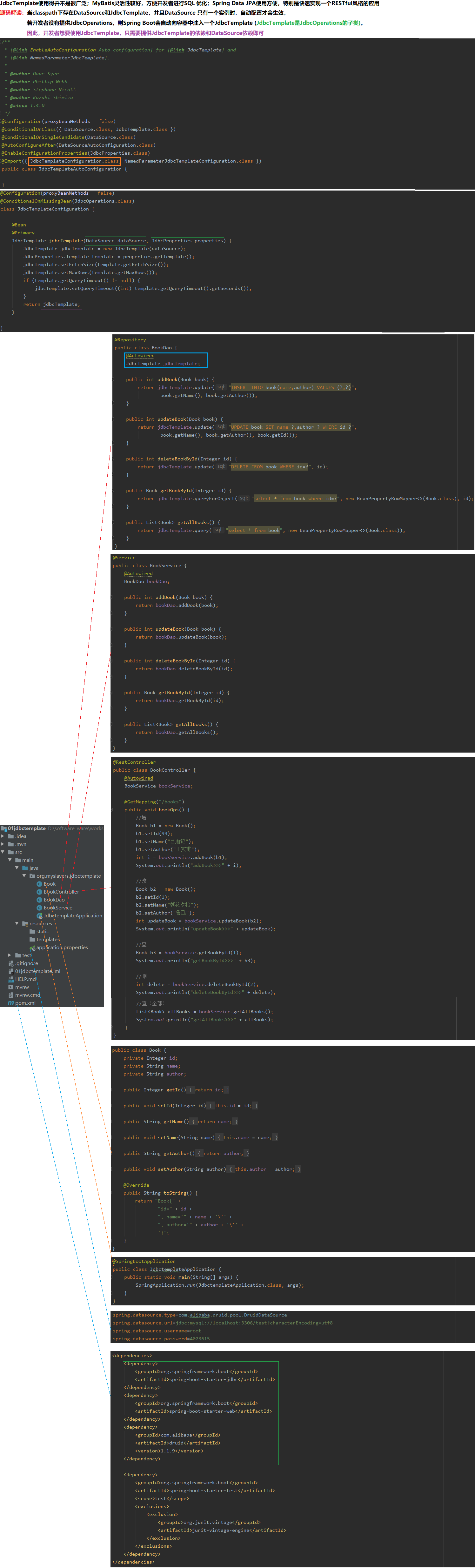
5.1 整合JdbcTempate
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.9</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=4023615
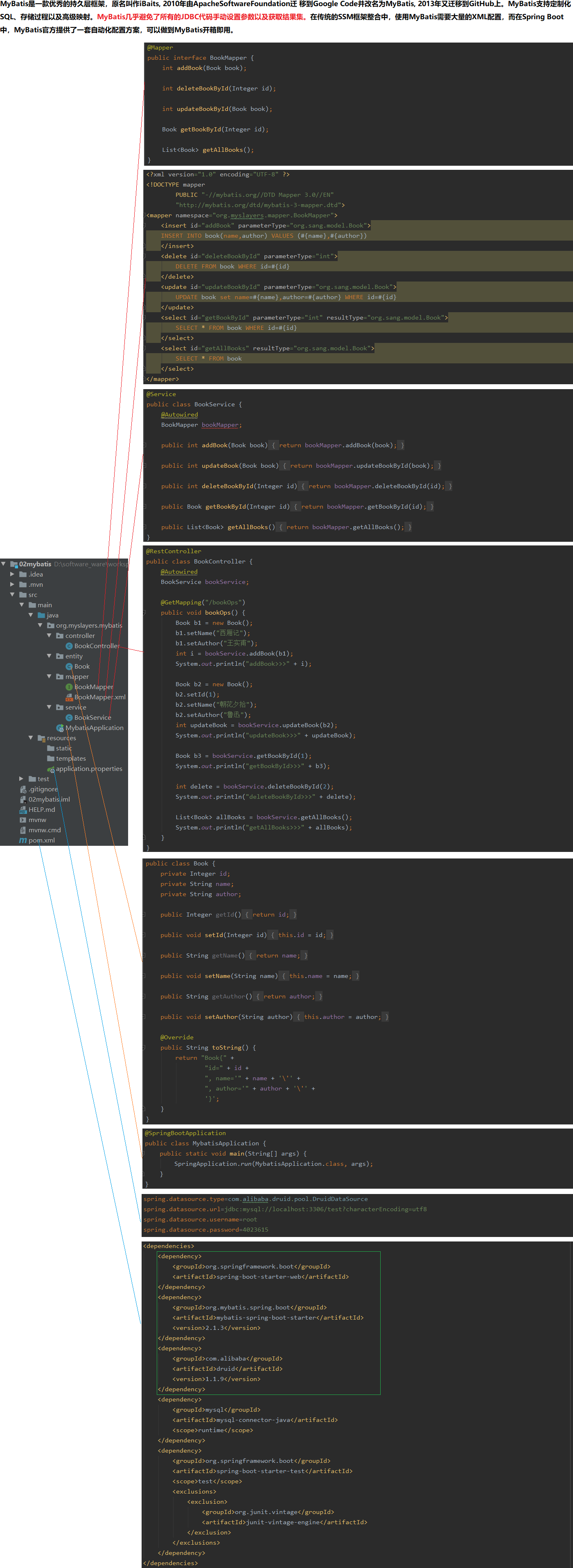
5.2 整合MyBatis
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
02.配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=4023615
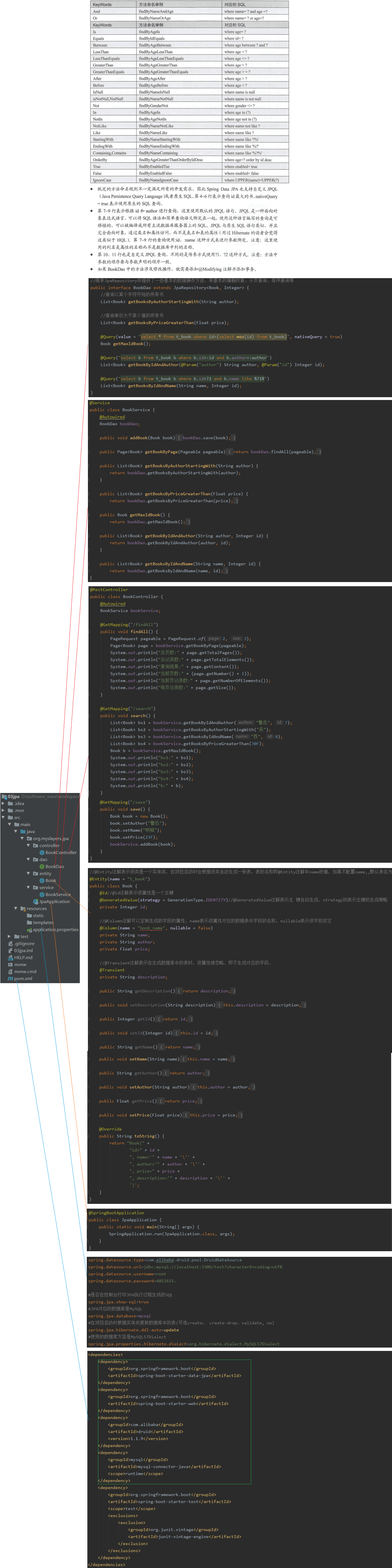
5.3 整合SpringDataJPA
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=4023615
#是否在控制台打印JPA执行过程生成的SQL
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
#JPA对应的数据库是MySQL
spring.jpa.database=mysql
#在项目启动时根据实体类更新数据库中的表(可选create、 create-drop、validate, no)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
#使用的数据库方言是MySQL57Dialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL57Dialect
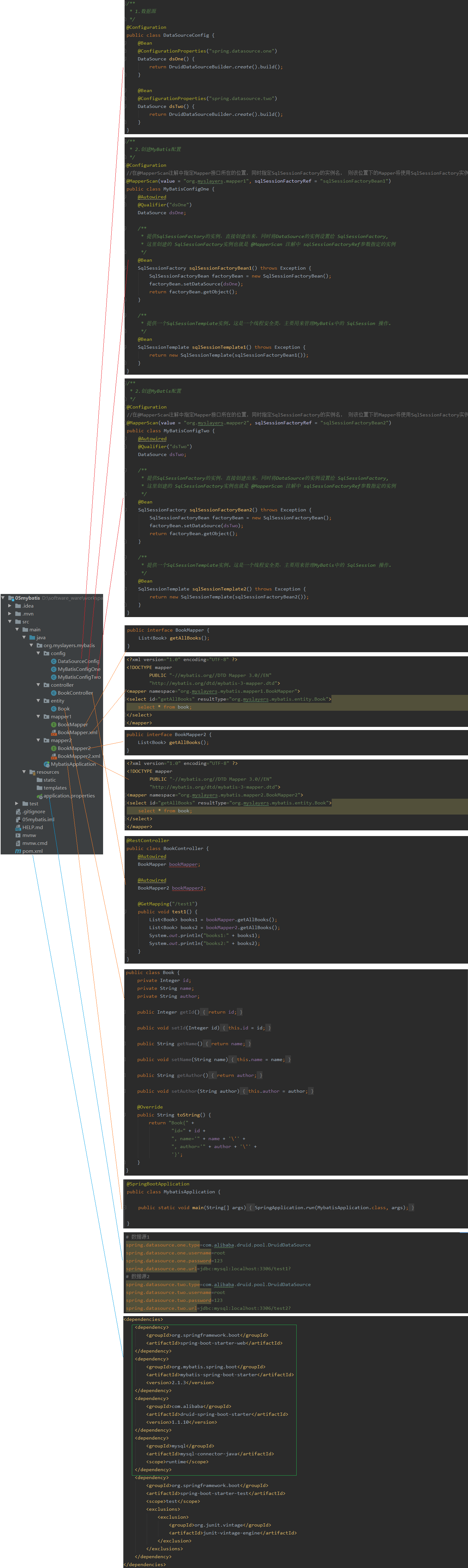
5.4 多数据源
5.4.1 JdbcTempate
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
# 数据源1
spring.datasource.one.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.one.username=root
spring.datasource.one.password=123
spring.datasource.one.url=jdbc:mysql:localhost:3306/test1?
# 数据源2
spring.datasource.two.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.two.username=root
spring.datasource.two.password=123
spring.datasource.two.url=jdbc:mysql:localhost:3306/test2?
5.4.2 MyBatis
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
02.配置
# 数据源1
spring.datasource.one.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.one.username=root
spring.datasource.one.password=123
spring.datasource.one.url=jdbc:mysql:localhost:3306/test1?
# 数据源2
spring.datasource.two.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.two.username=root
spring.datasource.two.password=123
spring.datasource.two.url=jdbc:mysql:localhost:3306/test2?
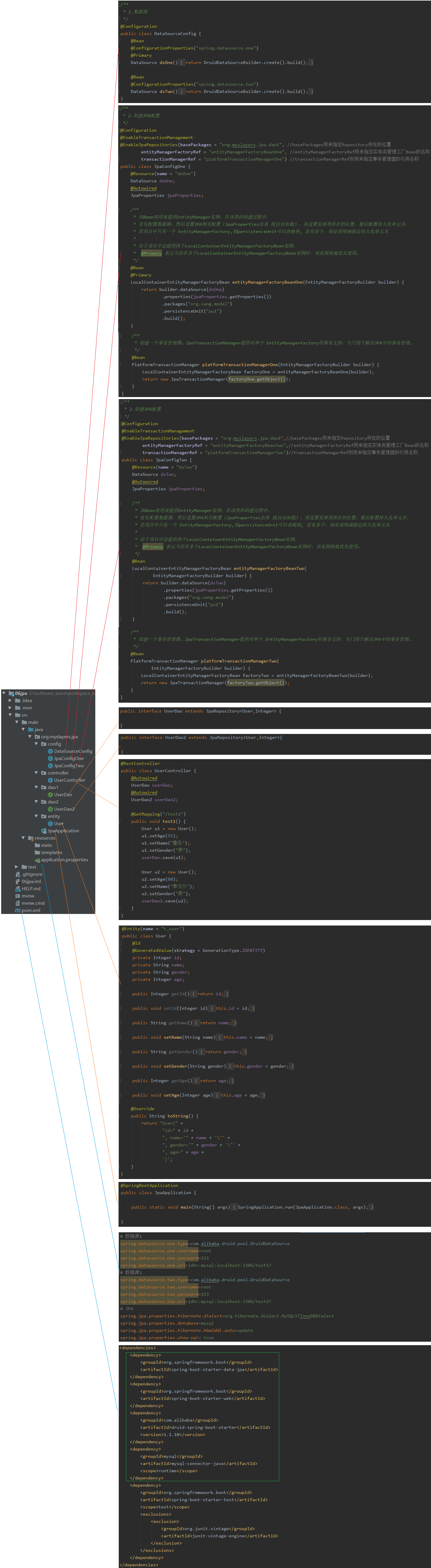
5.4.3 SpringDataJPA
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
# 数据源1
spring.datasource.one.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.one.username=root
spring.datasource.one.password=123
spring.datasource.one.url=jdbc:mysql:localhost:3306/test1?
# 数据源2
spring.datasource.two.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.two.username=root
spring.datasource.two.password=123
spring.datasource.two.url=jdbc:mysql:localhost:3306/test2?
# JPA
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL57InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.properties.database=mysql
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.show-sql= true
6 SpringBoot整合NoSQL
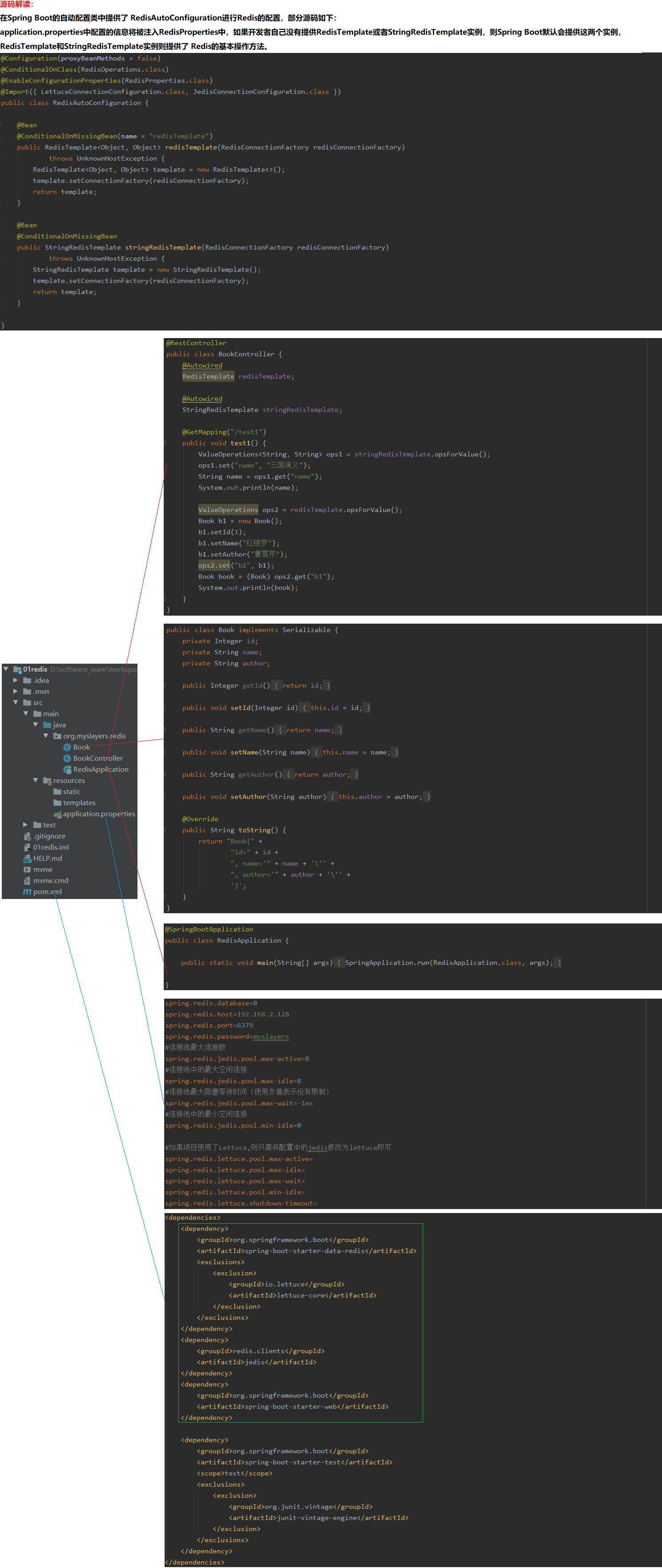
6.1 整合Redis
6.1.1 Redis单机版
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependencies>
02.配置
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.host=192.168.2.128
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=myslayers
#连接池最大连接数
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8
#连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=8
#连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1ms
#连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
#如果项目使用了Lettuce,则只需将配置中的jedis修改为lettuce即可
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=
spring.redis.lettuce.shutdown-timeout=
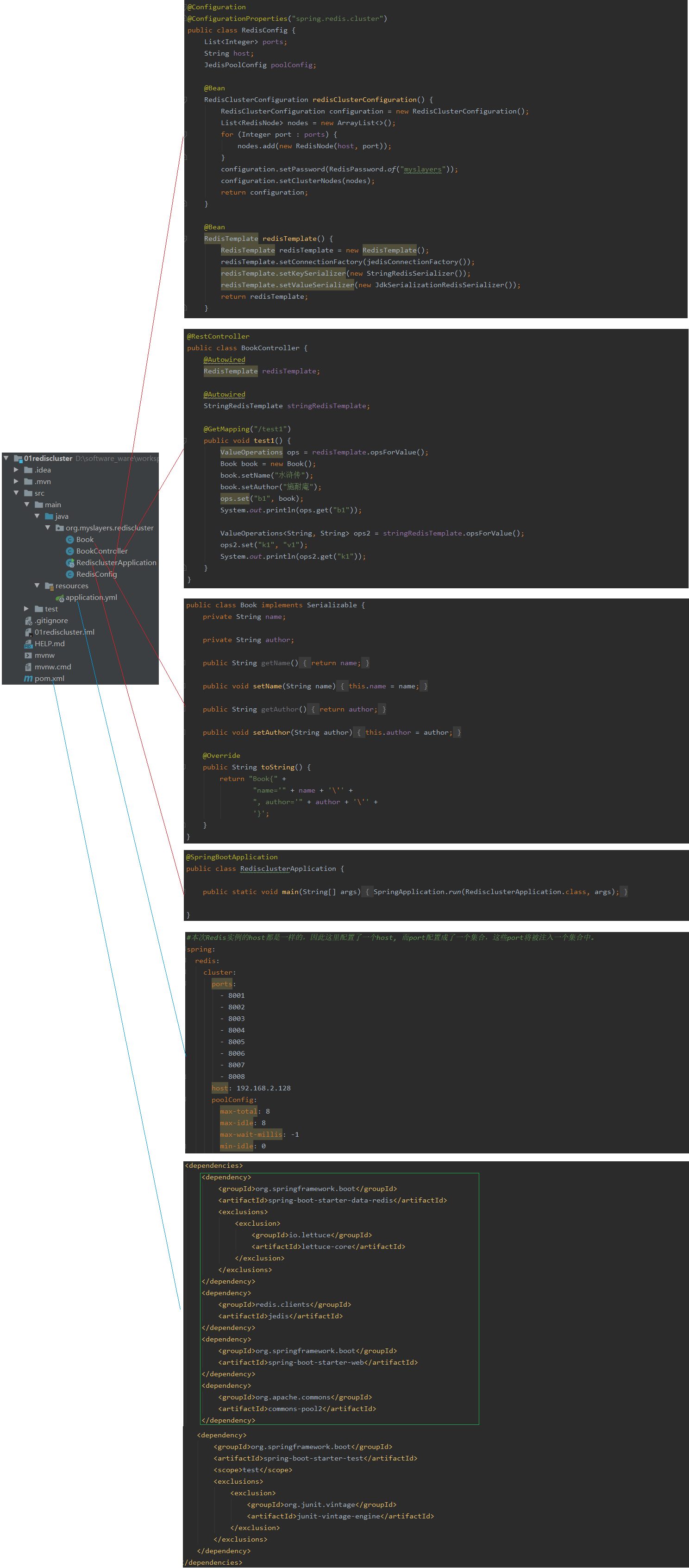
6.1.2 Redis集群
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependencies>
02.配置
spring:
redis:
cluster:
ports:
- 8001
- 8002
- 8003
- 8004
- 8005
- 8006
- 8007
- 8008
host: 192.168.2.128
poolConfig:
max-total: 8
max-idle: 8
max-wait-millis: -1
min-idle: 0
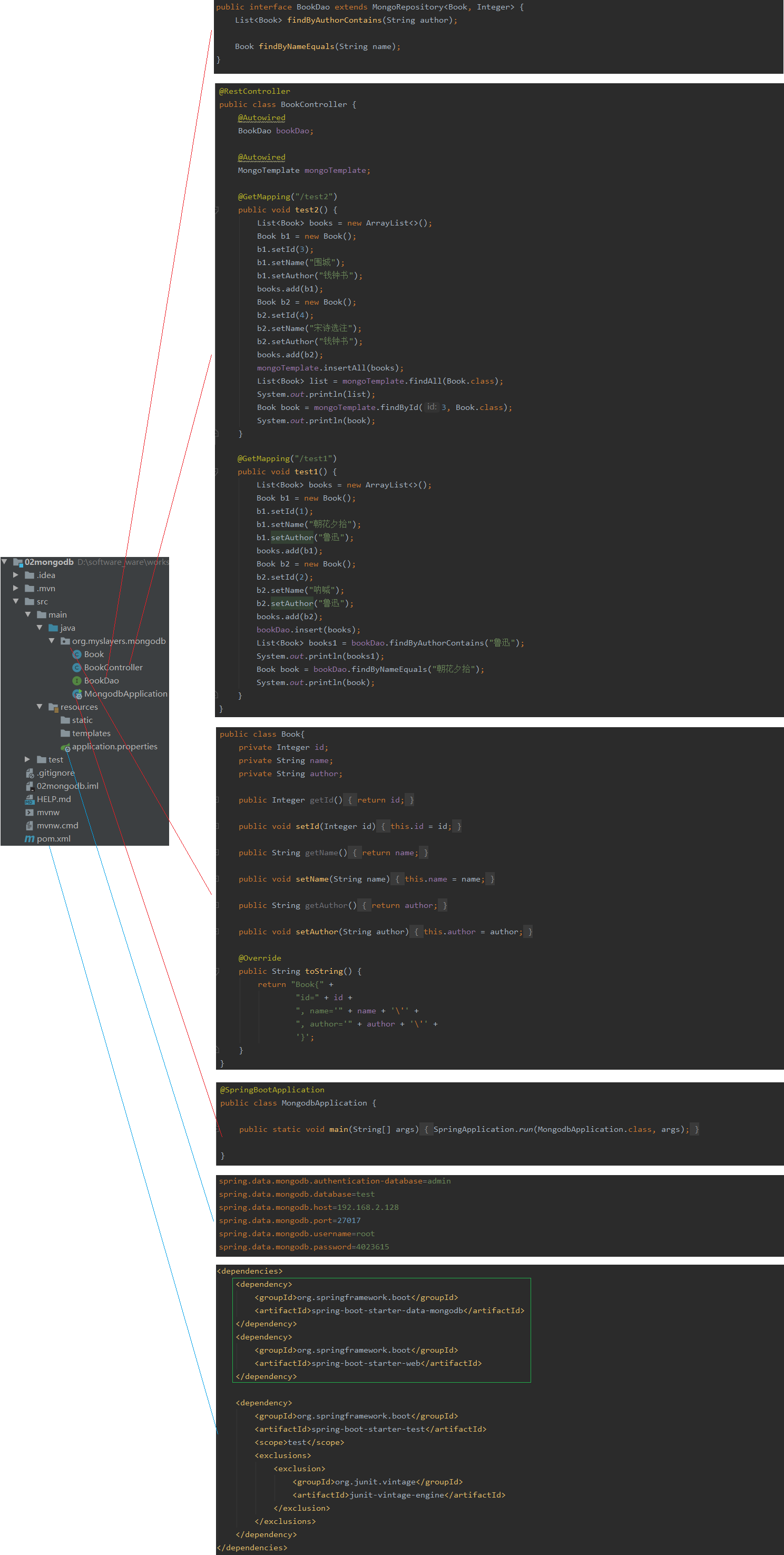
6.2 整合MongoDB
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring.data.mongodb.authentication-database=admin
spring.data.mongodb.database=test
spring.data.mongodb.host=192.168.2.128
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.data.mongodb.username=root
spring.data.mongodb.password=4023615
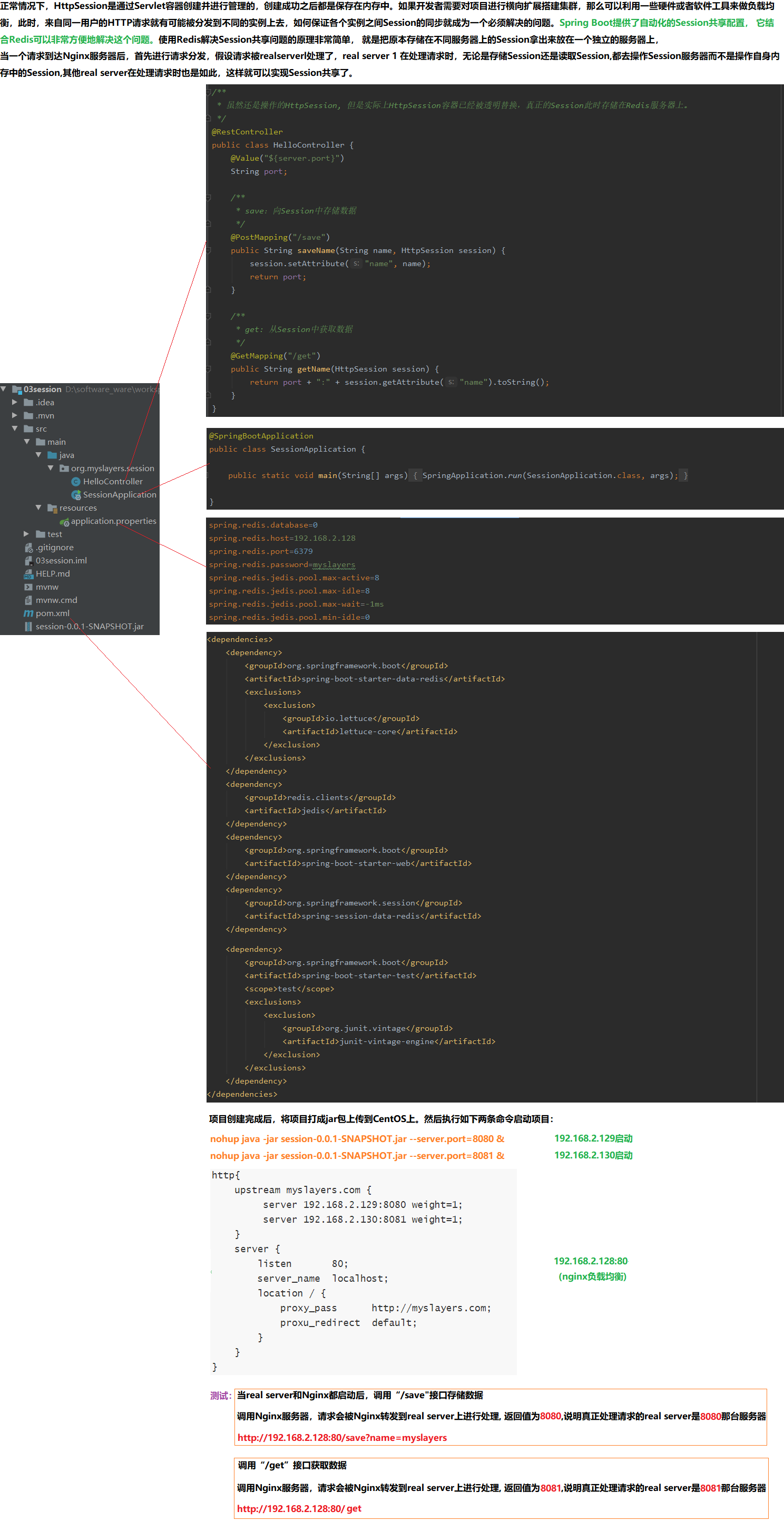
6.3 Session共享
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
a.下载
cd /usr/local
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
tar -zxvf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
b.依赖
yum install -y gcc pcre pcre-devel
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
c.编译
cd /usr/local/nginx-1.14.0 --打开目录
./configure
make
make install
d.启动
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx --启动Nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop --停止Nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload --重启Nginx
e.配置,负载均衡
vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user root; --解决权限
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http{
upstream myslayers.com {
server 192.168.2.129:8080 weight=1;
server 192.168.2.130:8081 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myslayers.com;
proxu_redirect default;
}
}
}
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload --重启nginx
f.开机自启
vi /etc/rc.local --打开文件
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx --追加
chmod 755 /etc/rc.local --设置文件权限
g.测试负载均衡
nohup java -jar session-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8080 &
nohup java -jar session-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8081 &
http://192.168.2.128:80/save?name=myslayers
http://192.168.2.128:80/get
7 构建RESTful服务
01.动作
GET (SELECT):从服务器检索特定资源,或资源列表。
POST (CREATE):在服务器上创建一个新的资源。
PUT (UPDATE):更新服务器上的资源,提供整个资源。
PATCH (UPDATE):更新服务器上的资源,仅提供更改的属性。
DELETE (DELETE):从服务器删除资源。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
首先是四个半种动作:
post、delete、put/patch、get
因为put/patch只能算作一类,所以将patch归为半个。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
另外还有有两个较少知名的HTTP动词:
HEAD - 检索有关资源的元数据,例如数据的哈希或上次更新时间。
OPTIONS - 检索关于客户端被允许对资源做什么的信息。
02.路径(接口命名)
路径又称"终点"(endpoint),表示API的具体网址。
在RESTful架构中,每个网址代表一种资源(resource),所以网址中不能有动词,只能有名词,而且所用的名词往往与数据库的表格名对应。一般来说,数据库中的表都是同种记录的"集合"(collection),所以API中的名词也应该使用复数。
举例来说,有一个API提供动物园(zoo)的信息,还包括各种动物和雇员的信息,则它的路径应该设计成下面这样。
GET /zoos:列出所有动物园
POST /zoos:新建一个动物园
GET /zoos/ID:获取某个指定动物园的信息
PUT /zoos/ID:更新某个指定动物园的信息(提供该动物园的全部信息)
PATCH /zoos/ID:更新某个指定动物园的信息(提供该动物园的部分信息)
DELETE /zoos/ID:删除某个动物园
GET /zoos/ID/animals:列出某个指定动物园的所有动物
DELETE /zoos/ID/animals/ID:删除某个指定动物园的指定动物
03.过滤信息(Filtering)
如果记录数量很多,服务器不可能都将它们返回给用户。API应该提供参数,过滤返回结果。
下面是一些常见的参数。
?limit=10:指定返回记录的数量
?offset=10:指定返回记录的开始位置。
?page_number=2&page_size=100:指定第几页,以及每页的记录数。
?sortby=name&order=asc:指定返回结果按照哪个属性排序,以及排序顺序。
?animal_type_id=1:指定筛选条件
参数的设计允许存在冗余,即允许API路径和URL参数偶尔有重复。比如,
GET /zoo/ID/animals 与 GET /animals?zoo_id=ID 的含义是相同的。
04.状态码(Status Codes)
1xx 信息,请求收到,继续处理。范围保留用于底层HTTP的东西,你很可能永远也用不到。
2xx 成功,行为被成功地接受、理解和采纳
3xx 重定向,为了完成请求,必须进一步执行的动作
4xx 客户端错误,请求包含语法错误或者请求无法实现。范围保留用于响应客户端做出的错误
5xx 范围的状态码是保留给服务器端错误用的。这些错误常常是从底层的函数抛出来的,甚至
开发人员也通常没法处理,发送这类状态码的目的以确保客户端获得某种响应。
当收到5xx响应时,客户端不可能知道服务器的状态,所以这类状态码是要尽可能的避免。
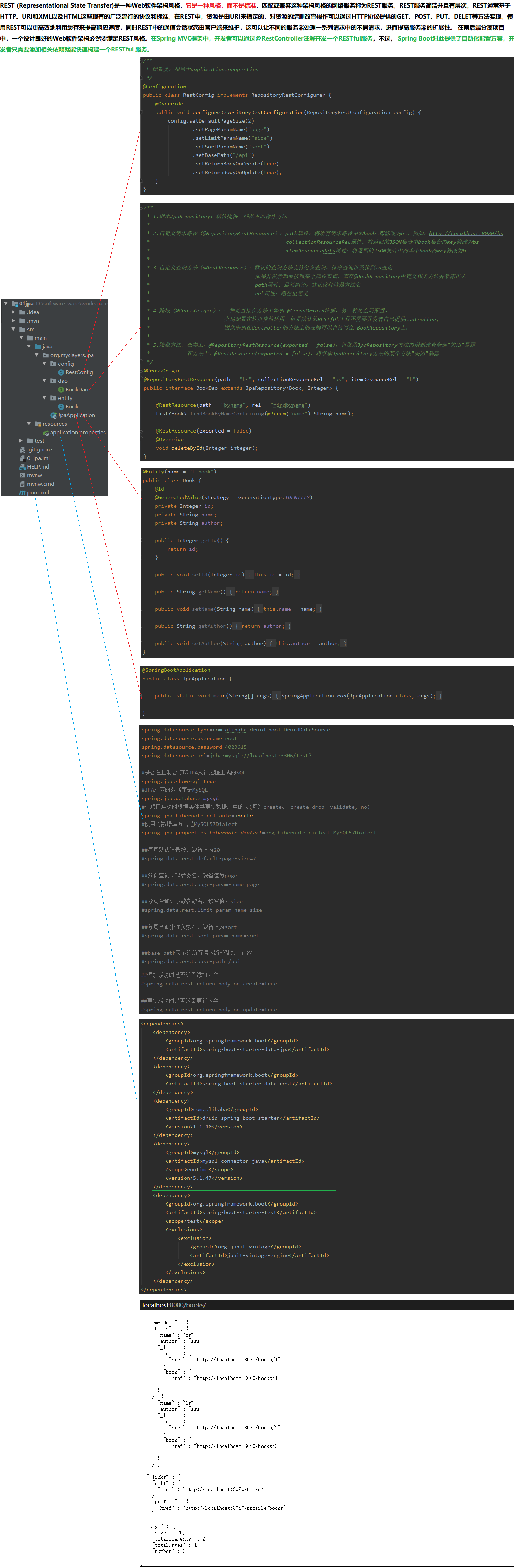
7.1 JPA实现REST
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=4023615
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?
#是否在控制台打印JPA执行过程生成的SQL
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
#JPA对应的数据库是MySQL
spring.jpa.database=mysql
#在项目启动时根据实体类更新数据库中的表(可选create、 create-drop、validate, no)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
#使用的数据库方言是MySQL57Dialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL57Dialect
##每页默认记录数,缺省值为20
#spring.data.rest.default-page-size=2
##分页查询页码参数名,缺省值为page
#spring.data.rest.page-param-name=page
##分页查询记录数参数名,缺省值为size
#spring.data.rest.limit-param-name=size
##分页查询排序参数名,缺省值为sort
#spring.data.rest.sort-param-name=sort
##base-path表示给所有请求路径都加上前缀
#spring.data.rest.base-path=/api
##添加成功时是否返回添加内容
#spring.data.rest.return-body-on-create=true
##更新成功时是否返回更新内容
#spring.data.rest.return-body-on-update=true
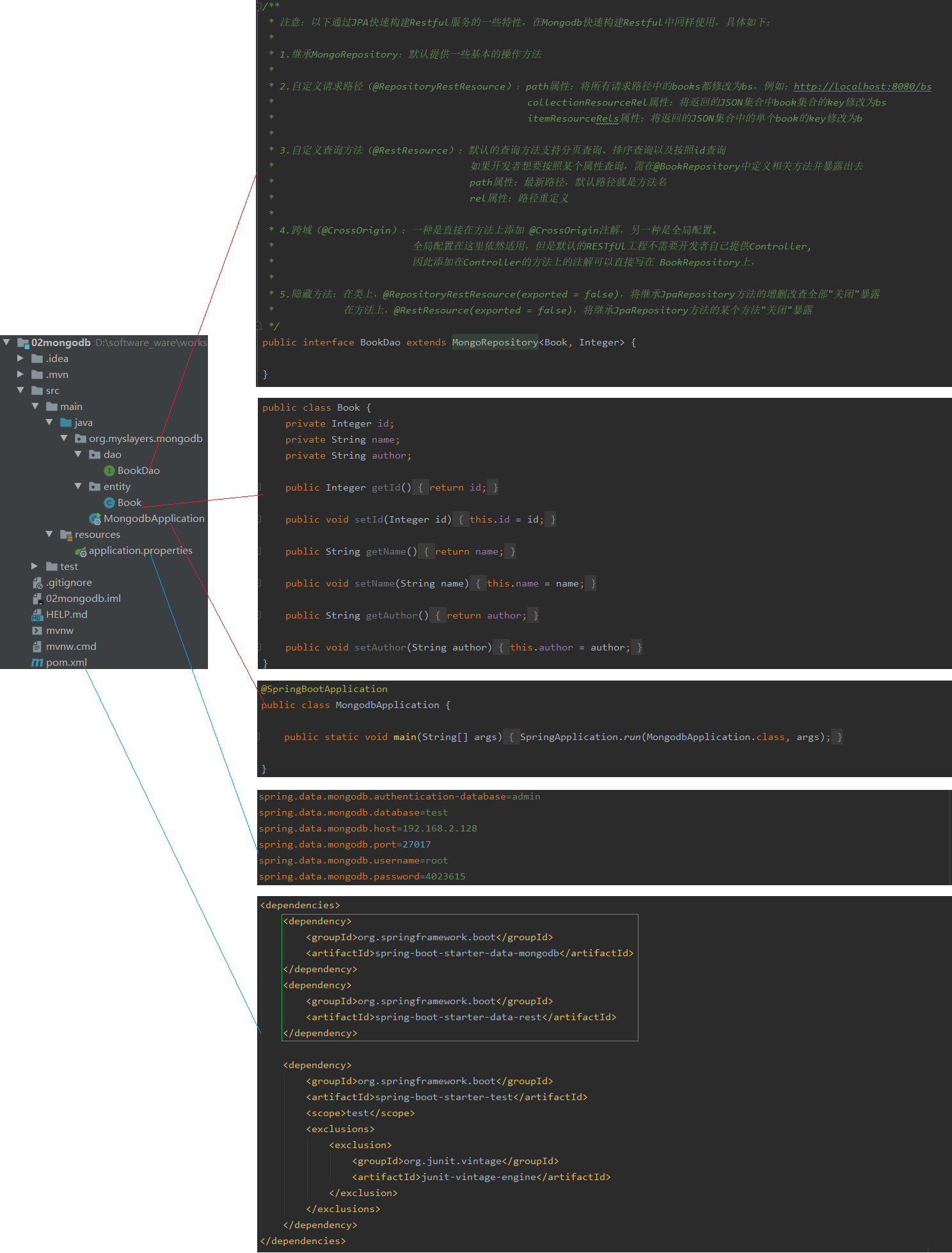
7.2 MongoDB实现REST
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring.data.mongodb.authentication-database=admin
spring.data.mongodb.database=test
spring.data.mongodb.host=192.168.2.128
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.data.mongodb.username=root
spring.data.mongodb.password=4023615
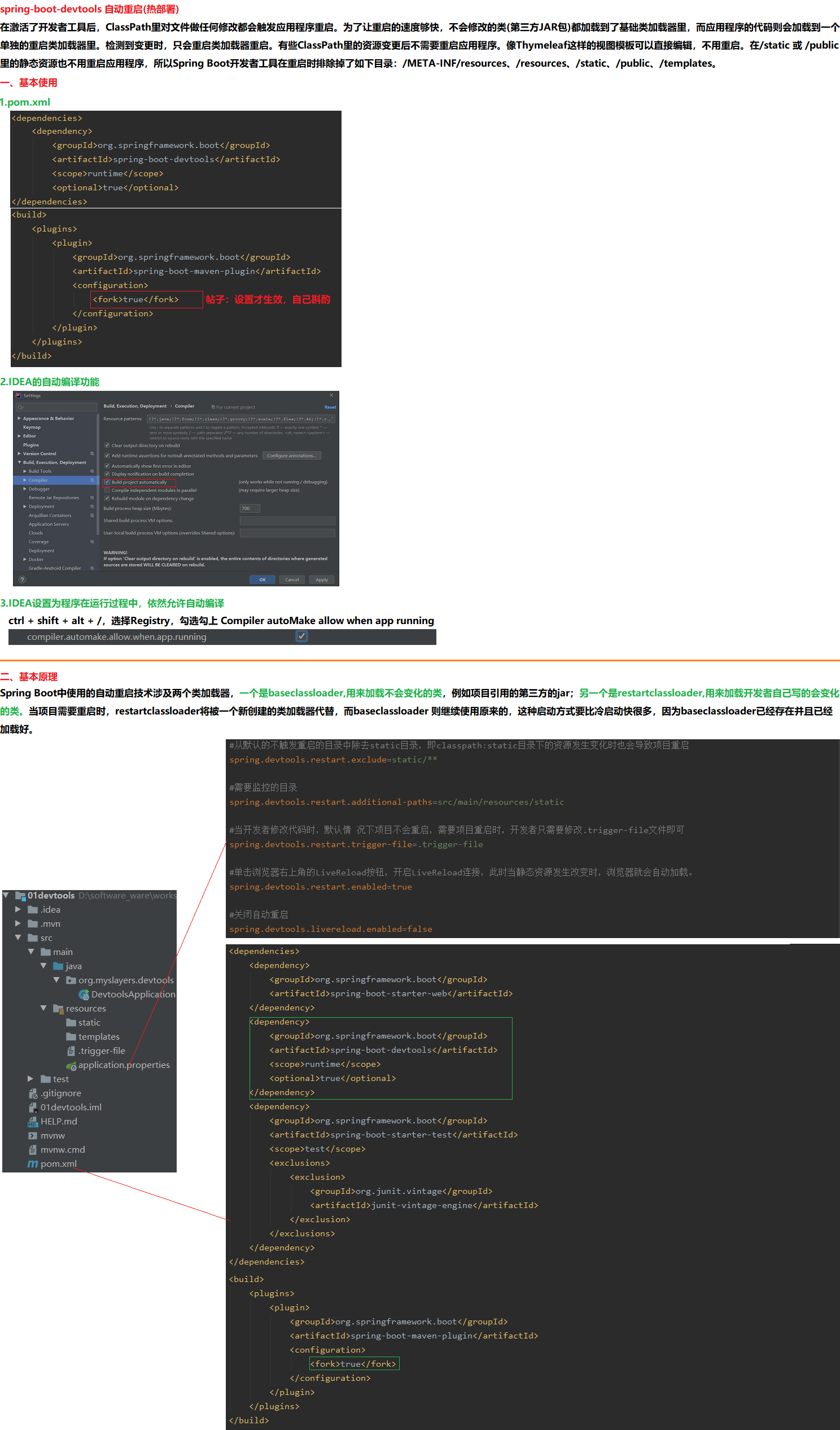
8 开发者工具与单元测试
01.依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
02.配置
#从默认的不触发重启的目录中除去static目录,即classpath:static目录下的资源发生变化时也会导致项目重启
spring.devtools.restart.exclude=static/**
#需要监控的目录
spring.devtools.restart.additional-paths=src/main/resources/static
#当开发者修改代码时,默认情 况下项目不会重启,需要项目重启时,开发者只需要修改.trigger-file文件即可
spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file=.trigger-file
#单击浏览器右上角的LiveReload按钮,开启LiveReload连接,此时当静态资源发生改变时,浏览器就会自动加载
spring.devtools.restart.enabled=true
#关闭自动重启
spring.devtools.livereload.enabled=false
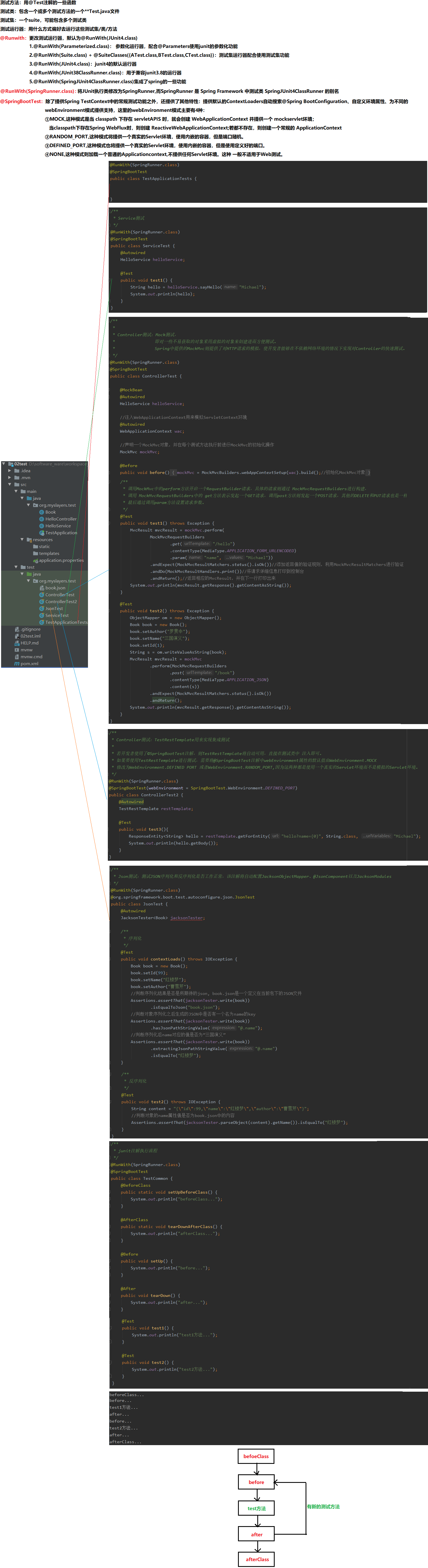
8.2 单元测试
01.单元测试
每一个测试方法上使用@Test进行修饰
每一个测试方法必须使用public void 进行修饰
每一个测试方法不能携带参数
测试代码和源代码在两个不同的项目路径下
测试类的包应该和被测试类保持一致
测试单元中的每个方法必须可以独立测试
以上的6条规则,是在使用单元测试的必须项,当然junit也建议我们在每一个测试方法名加上test前缀,表明这是一个测试方法。assertEquals是一个断言的规则,里面有两个参数,第一个参数表明我们预期的值,第二个参数表示实际运行的值。
02.注解说明
@Test:定义一个测试方法,测试方法必须是public void,即公共、无返回数据,可以抛出异常
@Test(timeout = 1000):测试方法执行超过1000毫秒后超时,测试将以失败而停止
@Test(expected = Exception.class):测试方法期望得到的异常类
@Ignore:暂时不运行某些测试方法或测试类
@BeforeClass:在测试类里所有用例运行之前,只运行一次这个方法。例如创建数据库连接、读取文件等。
方法名可以任意,但必须是public static void,即公开、静态、无返回
@AfterClass:在测试类里所有用例运行之后,运行一次。用于处理一些测试后续工作,例如清理数据,恢复现场。
方法名可以任意,但必须是public static void,即公开、静态、无返回
@Before:每个用例运行之前都运行一次。主要用于一些独立于用例之间的准备工作。
比如两个用例都需要读取数据库里的用户A信息,但第一个用例会删除A,而第二个用例需要修改A。
场景:@BeforeClass创建数据库连接,@Before来插入一条用户A信息。
方法名可以任意,但必须是public void,不能为static。不止运行一次,根据用例数而定。
@After:每个用例运行之后都运行一次。
方法名可以任意,但必须是public void,不能为static。不止运行一次,根据用例数而定。
@Runwith:更改测试运行器,默认为@RunWith(JUnit4.class)
@Parameters:用于使用参数化功能
9 SpringBoot缓存
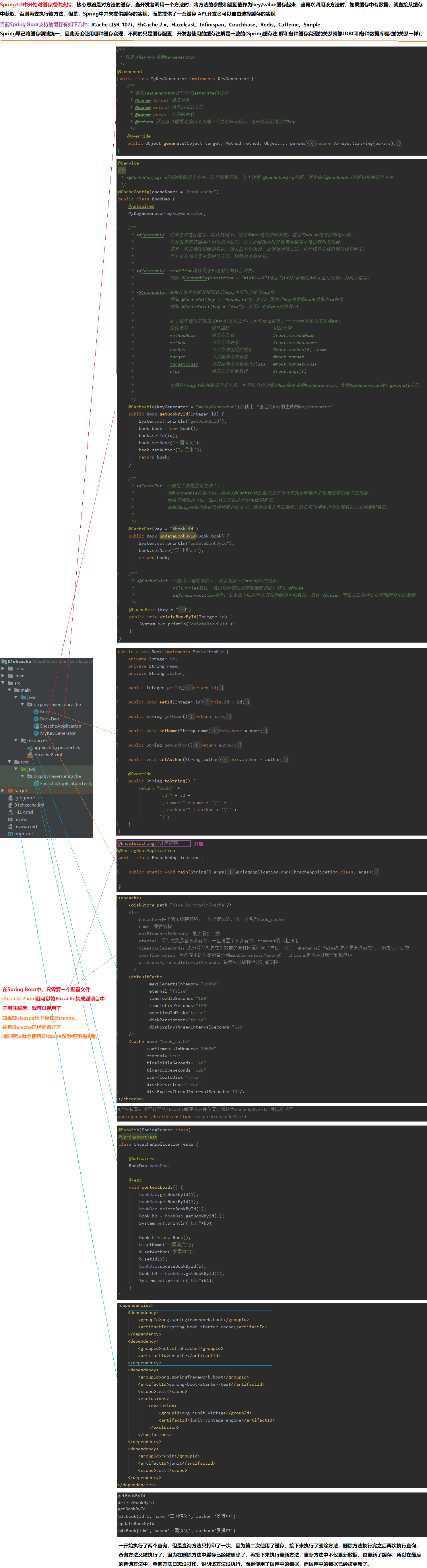
9.1 Ehcache 2.x缓存
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<ehcache>
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/cache"/>
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
/>
<cache name="book_cache"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
overflowToDisk="true"
diskPersistent="true"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="10"/>
</ehcache>
02.配置
#如果在classpath下存在Ehcache,并且Ehcache巳经配置好了,此时默认就会使用EhcacheManager作为缓存提供者
#缓存配置
spring.cache.cache-names=c1,c2
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=1800s
@EnableCaching//开启缓存
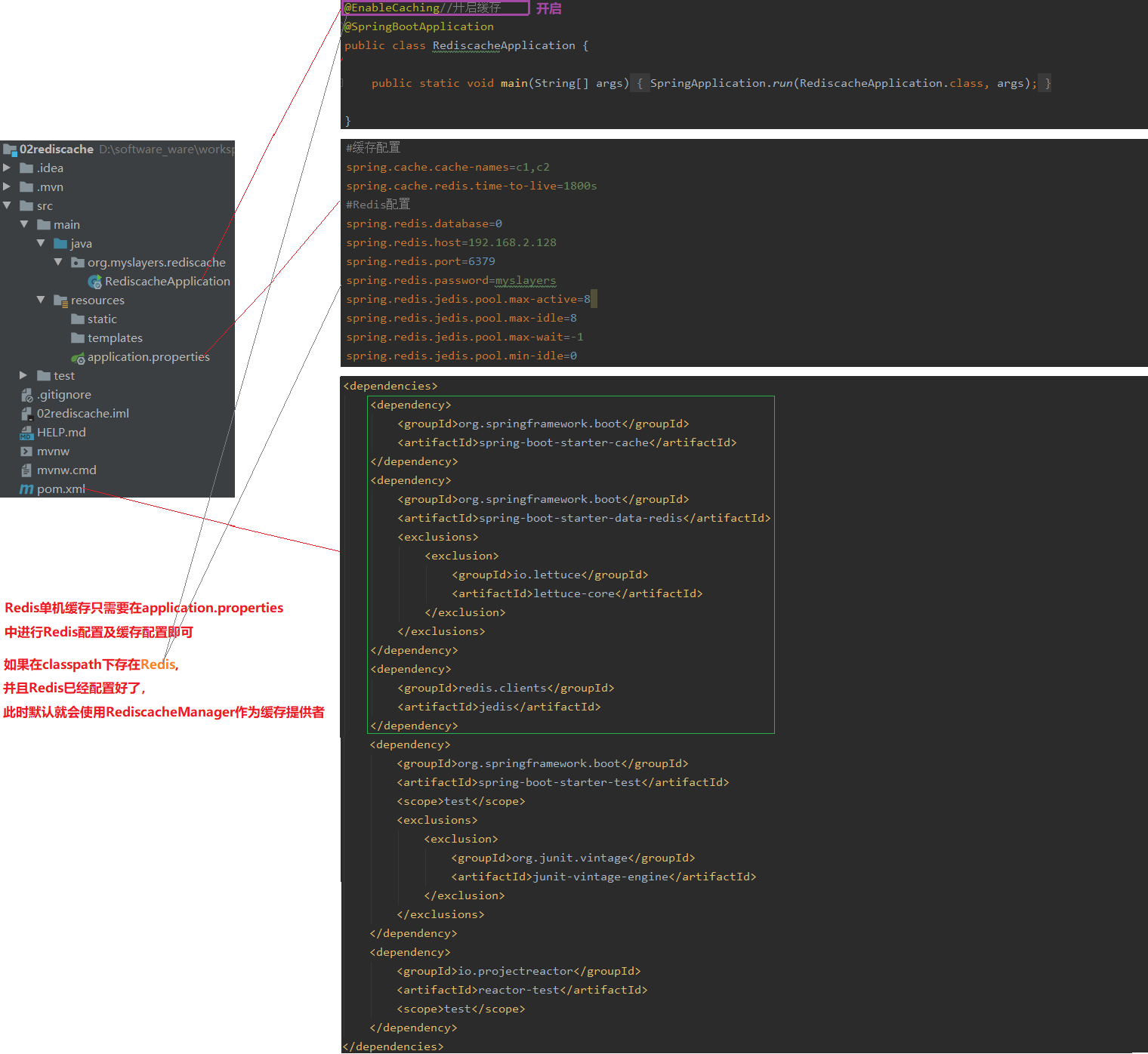
9.2 Redis单机缓存
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
#Redis单机缓存只需要在application.properties中进行Redis配置及缓存配置即可
#缓存配置
spring.cache.cache-names=c1,c2
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=1800s
#Redis配置
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.host=192.168.2.128
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=myslayers
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=8
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
@EnableCaching//开启缓存
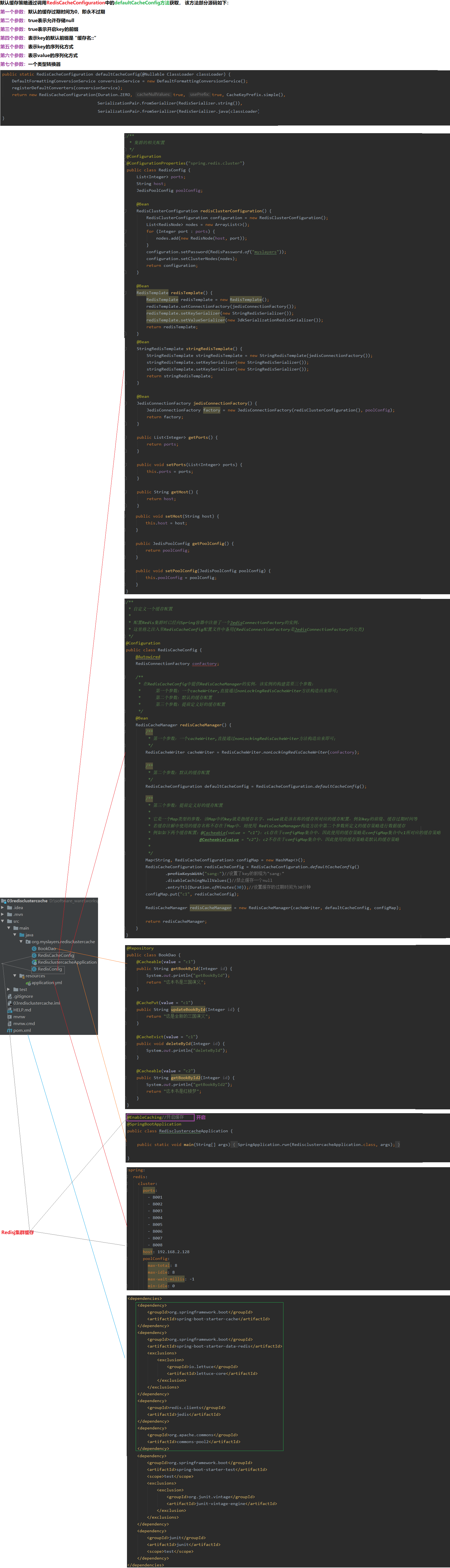
9.3 Redis集群缓存
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring:
redis:
cluster:
ports:
- 8001
- 8002
- 8003
- 8004
- 8005
- 8006
- 8007
- 8008
host: 192.168.2.128
poolConfig:
max-total: 8
max-idle: 8
max-wait-millis: -1
min-idle: 0
@EnableCaching//开启缓存
RedisConfig + RedisCacheConfig:集群配置类
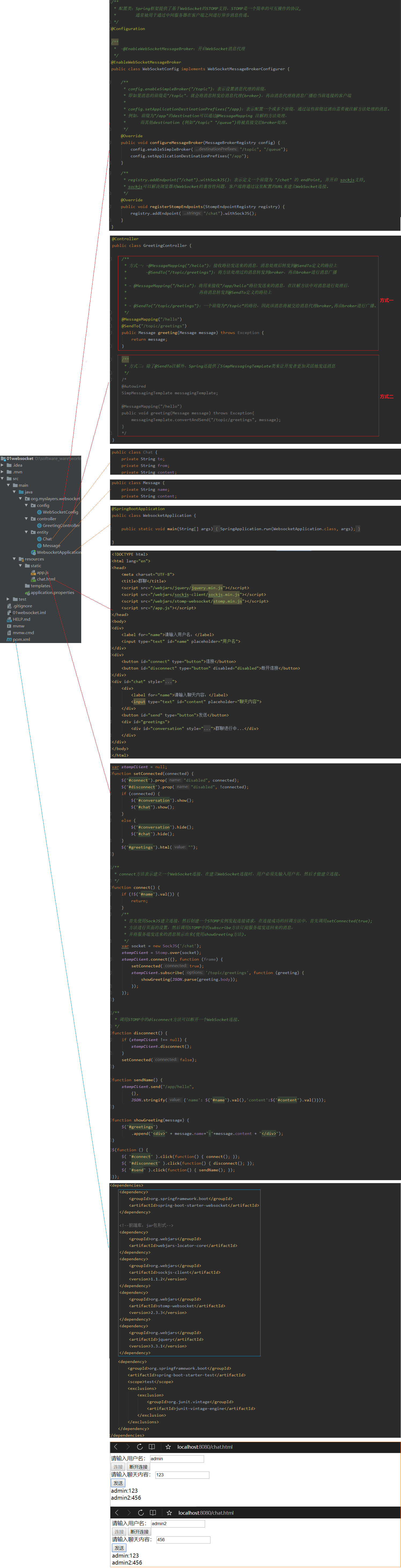
10 SpringBoot整合WebSocket
10.1 WebSocket
10.2 整合WebSocket
10.2.1 消息群发
01.方式一
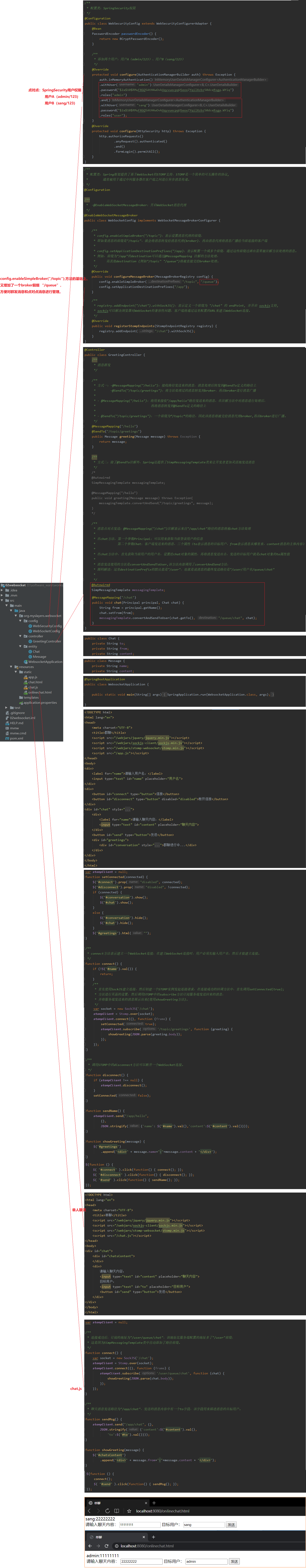
@MessageMapping("/hello"):接收路径发送来的消息,消息处理后转发到@SendTo定义的路径上
@SendTo("/topic/greetings"):将方法处理过的消息转发到broker,再由broker进行消息广播
02.方式二
除了@SendTo注解外,Spring还提供了SimpMessagingTemplate类来让开发者更加灵活地发送消息
10.2.2 消息点对点发送
00.SpringSecurity用户权限
admin/123、sang/123
11 消息服务
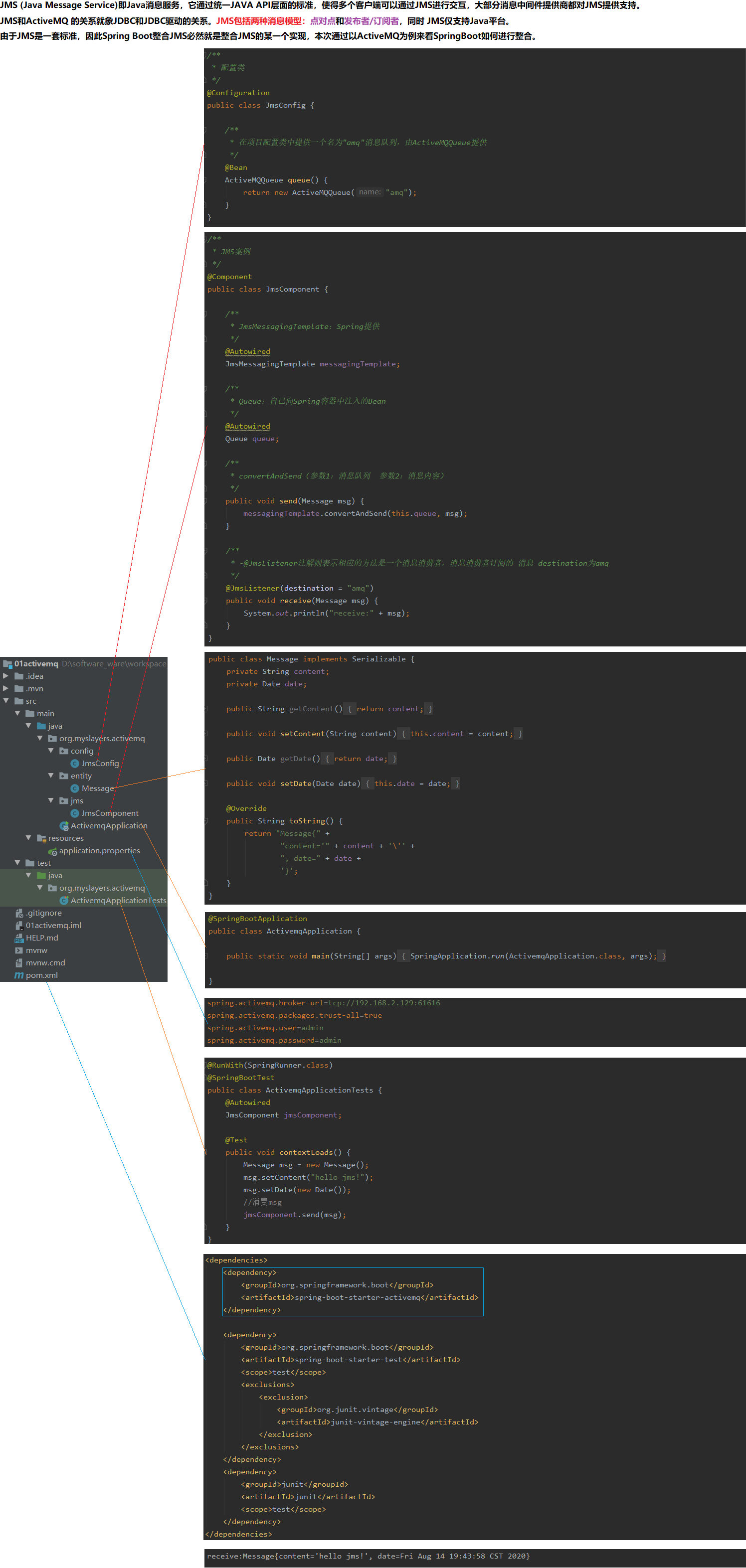
11.1 JMS
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://192.168.2.129:61616
spring.activemq.packages.trust-all=true
spring.activemq.user=admin
spring.activemq.password=admin
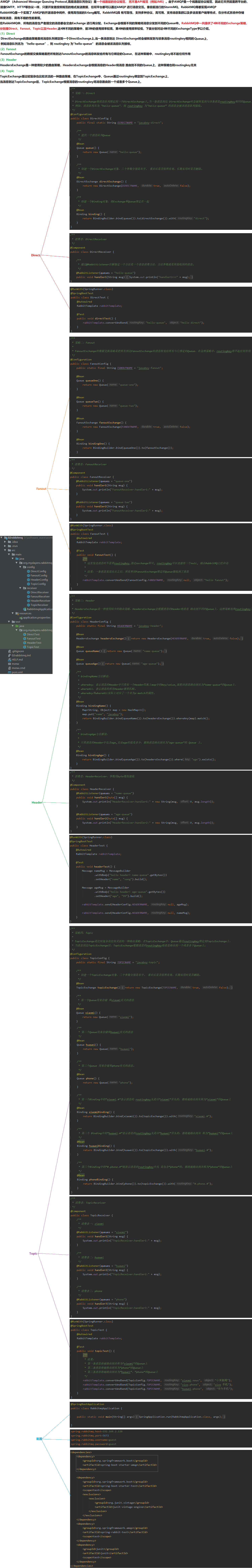
11.2 AMQP
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
#SpringBoot集成RabbitMQ,需要将15672改为5672(帖子)
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.2.128
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
12 企业开发
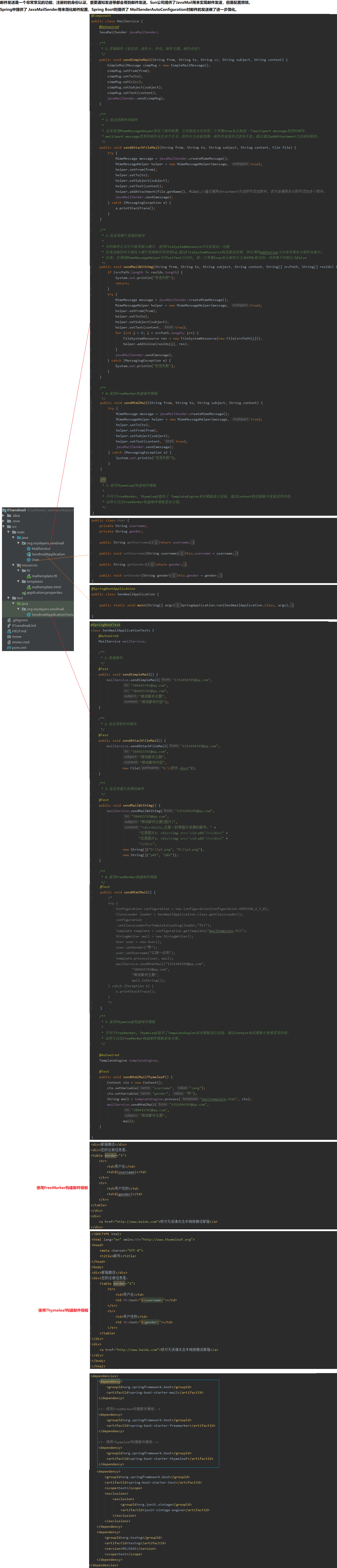
12.1 邮件发送
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--使用FreeMarker构建邮件模板-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--使用Thymeleaf构建邮件模板-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.功能
1.普通邮件
2.发送带附件的邮件
3.发送带图片资源的邮件
4.使用FreeMarker构建邮件模板
5.使用Thymeleaf构建邮件模板
12.2 定时任务
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.功能
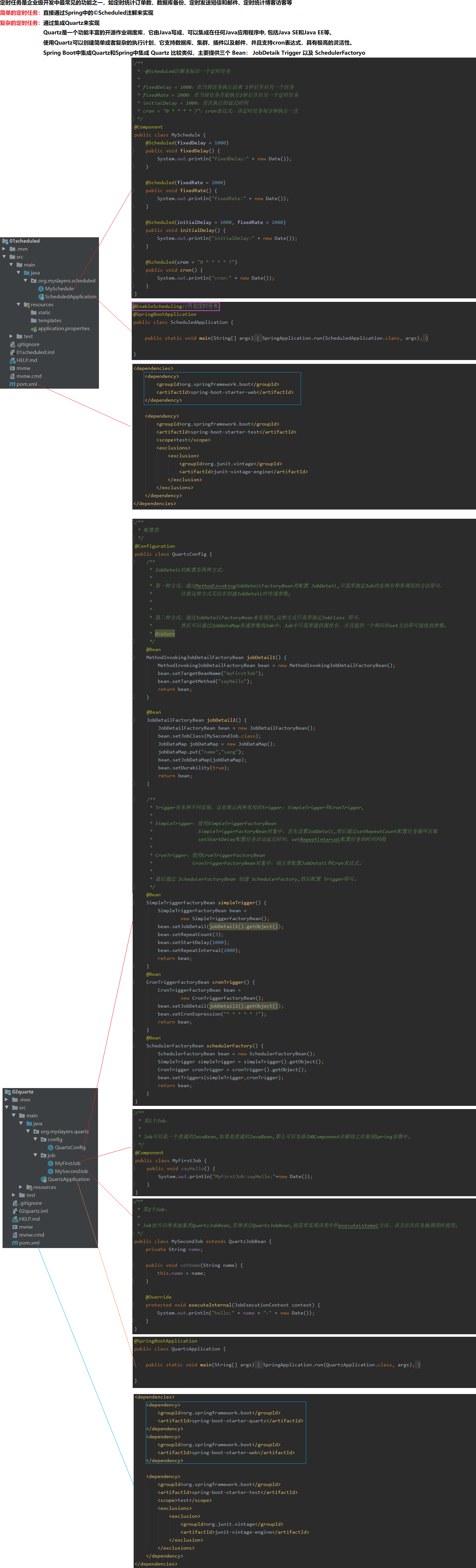
简单的定时任务:直接通过Spring中的@Scheduled注解来实现
复杂的定时任务:通过集成Quartz来实现
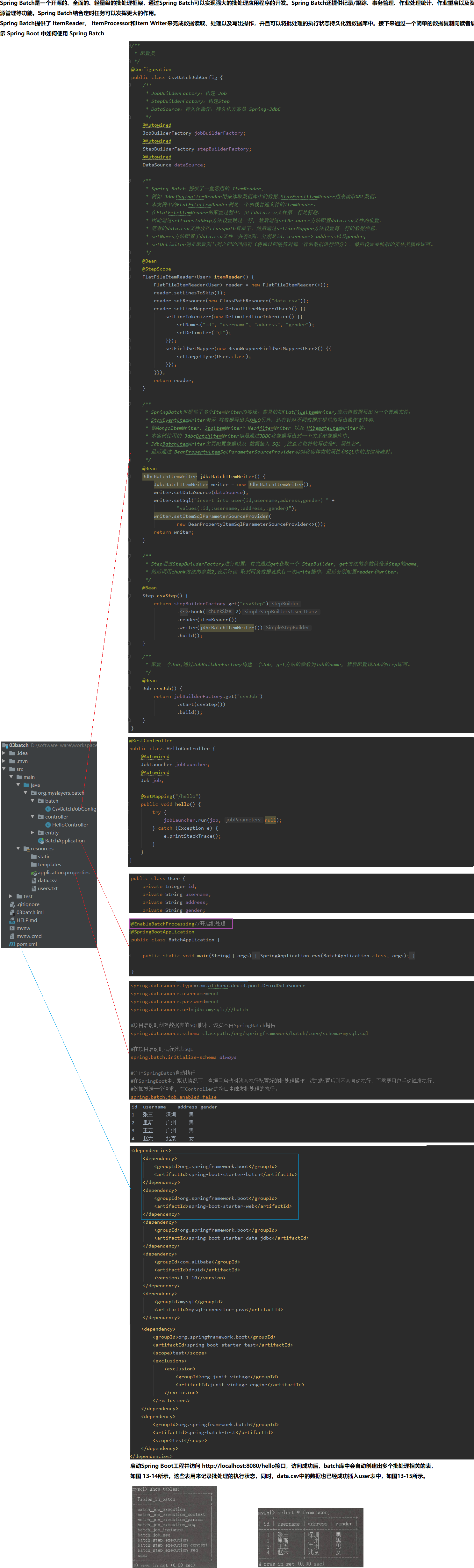
12.3 批处理
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
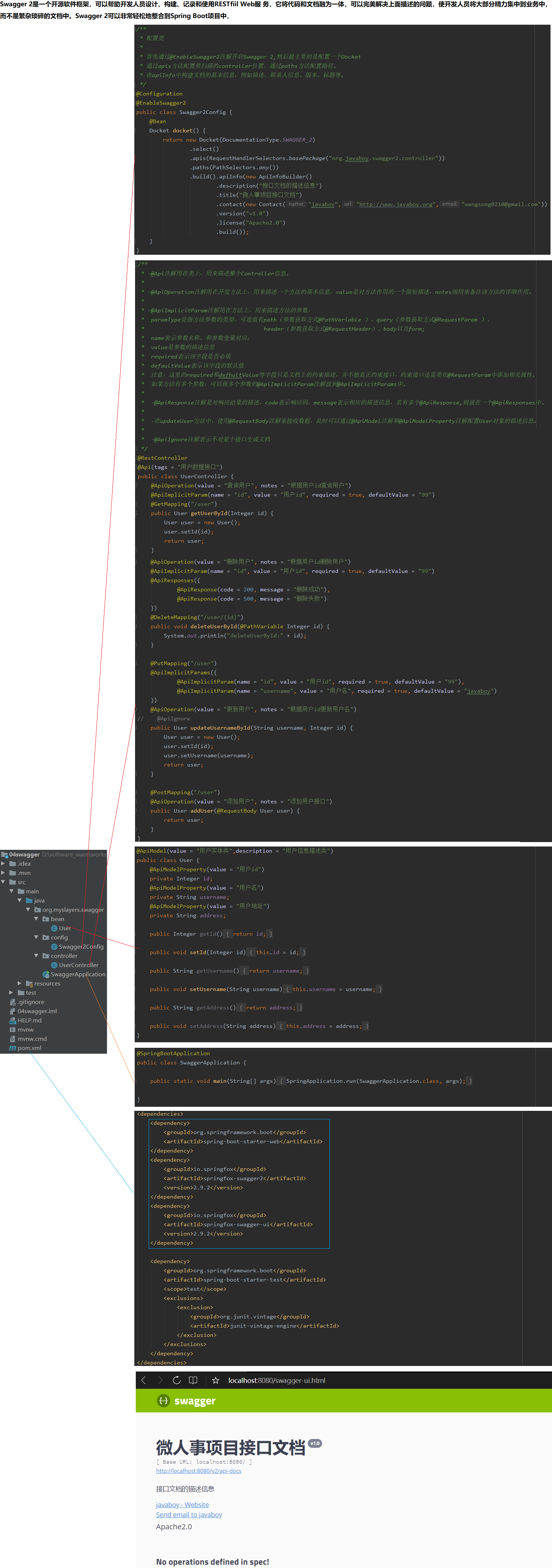
12.4 Swagger2
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
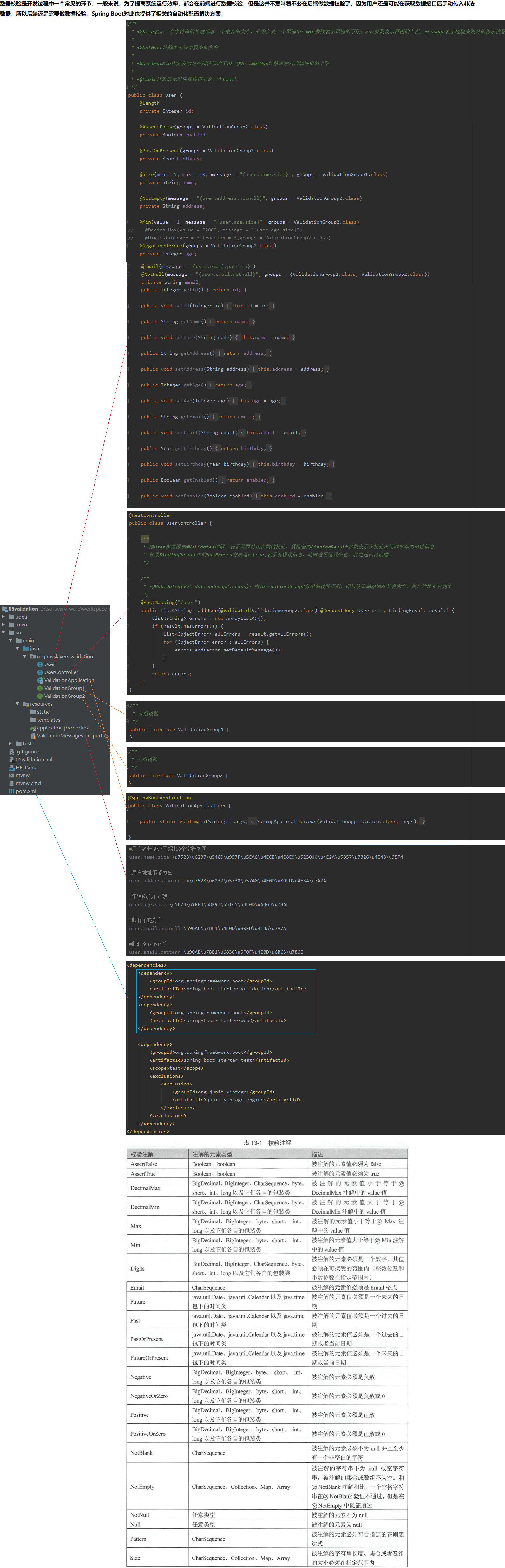
12.5 数据校验
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
13 应用监控
13.1 监控端点配置
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
#这些端点大部分都是默认开启的,只有shutdown端点默认未开启,通过下面这行开启
management.endpoint.sessions.enabled=true
#如果开发者不想暴露这么多端点,那么可以关闭默认的配置,然后手动指定需要开启哪些端点,如下配置表示关闭所有端点,只开启info端点:
#management.endpoints.enabled-by-default=false
#management.endpoint.info.enabled=true
#开发者可以在配置文件中自定义需要暴露哪些端点,例如要暴露mappings和metrics端点,添加如下配置
#management.endpoints.web.exposure.inc1ude=mappings,metrics
#如果要暴露所有端点,添加如下配置即可:
#management.endpoints.web.exposure.inc1ude=*
#测试端点保护
#spring.security.user.name=myslayers
#spring.security.user.password=4023615
#spring.security.user.roles=admin
#对于一些不带参数的端点请求会自动进行缓存,开发者可通过如下方式配置缓存时间:
#这个配置表示beans端点的缓存时间为100s,如果要配置其他端点,只需将beans修改为其他端点名称即可。
#注意,如果端点添加了Spring Security保护,此时Principal会被视为端点的输入,因此端点响应将不被缓存。
management.endpoint.beans.cache.time-to-live=100s
#默认情况下,所有端点都暴露在“/actuator”路径下,如果开发者需要对端点路径进行定制,可通过如下配置进行:
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/
2management.endpoints.web.path-mapping.health=healthcheck
#所有端点默认都没有开启跨域,开发者可以通过如下配置快速开启CORS支持,进而实现跨域
#这个配置表示允许端点处理来自http://localhost:8081地址的请求,允许的请求方法为GET和POST
1management.endpoints.web.cors.allowed-origins=http://localhost:8081
2management.endpoints.web.cors.allowed-methods=GET,POST
#展示健康信息详情
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
spring.security.user.name=myslayers
spring.security.user.password=4023615
spring.security.user.roles=admin
#若开发者不需要这么多Healthindicators,则可以通过如下配置关闭所有的Healthindicators自动化配置:
management.health.defaults.enabled=false
#如果开发者想要增加响应状态FATAL,在application.properties中增加如下配置:
management.health.status.order=FATAL,DOWN,OUT OF SERVICE,UP,UNKNOWN
#如果开发者需要对自定义的响应状态配置响应码,添加如下配置即可:
management.health.status.http-mapping.FATAL=503
#自定义信息
info.app.encoding=@project.build.sourceEncoding@
info.app.java.source=@java.version@
info.app.java.target=@java.version@
info.author.name=\u6C5F\u5357\u4E00\u70B9\u96E8
info.author.email=wangsong0210@gmail.com
#展示所有的 Git 交信息
management.info.git.mode=full
13.2 监控信息可视化
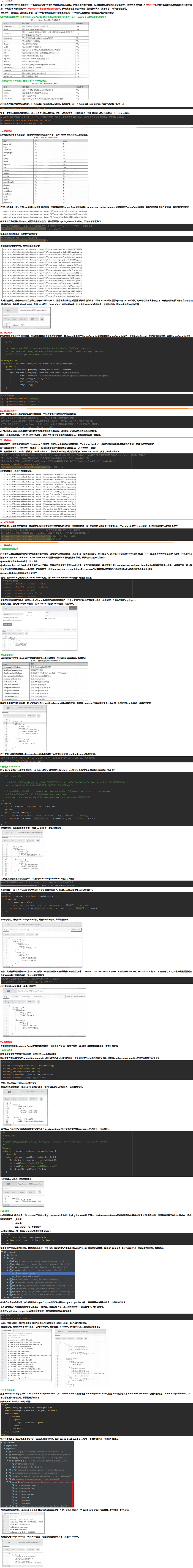
01.服务端
a.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
b.配置
@EnableAdminServer添加在启动类上,启动AdminServer
02.客户端
a.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
b.配置
#Client实际上就是一个一个服务,然后将被注册到AdminServer,AdminServer获取Client的运行数据后展示
server.port=8080
spring.boot.admin.client.url=http://localhost:8081
03.测试
http://localhost:8080/index.html
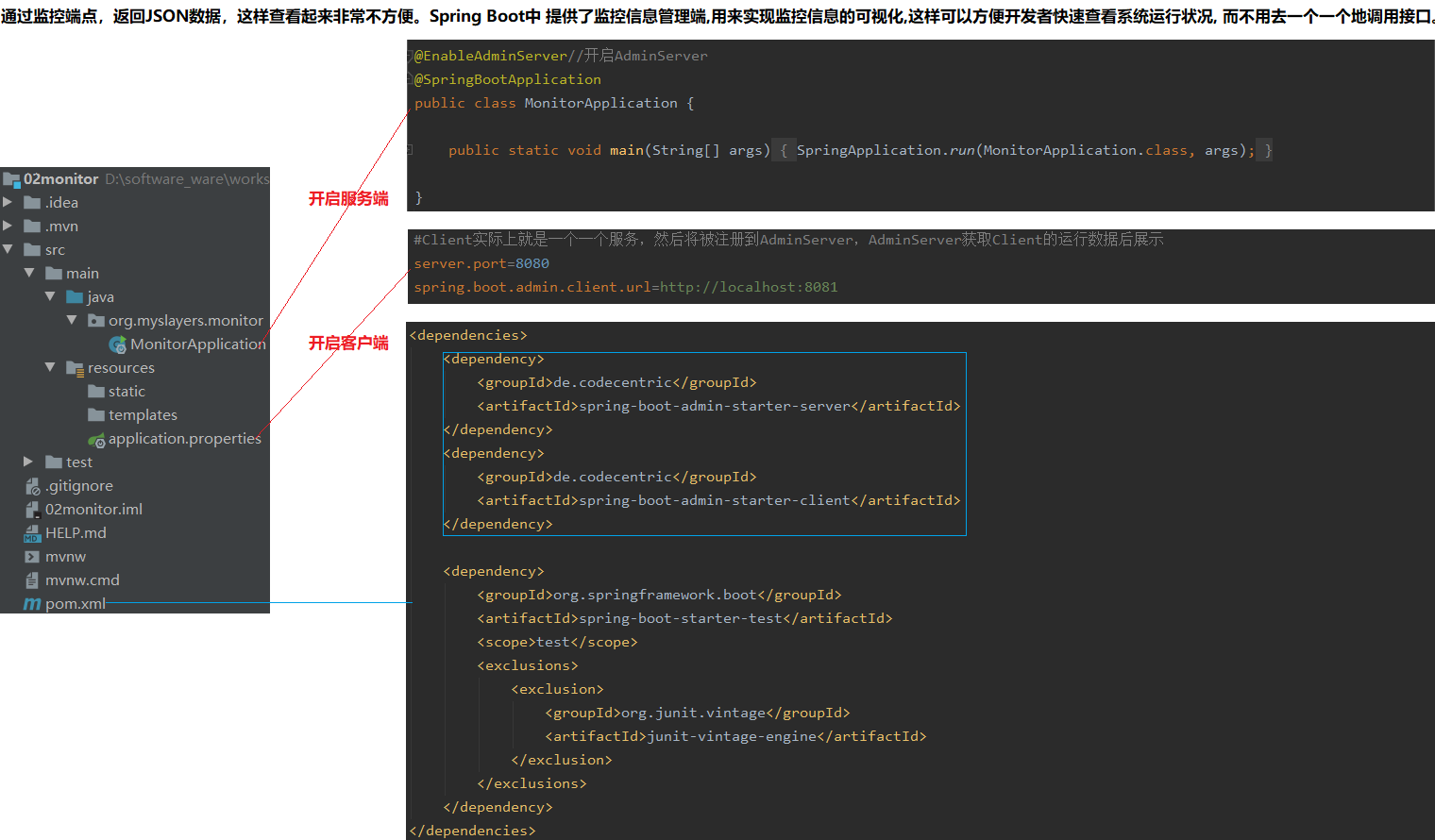
13.3 邮件报警
01.依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
#邮件报警:默认情况下,当被监控应用的状态变为UNKNOWN或者UP时不会发送报警邮件,这里的配置表示被监控应用的任何变化都会发送报警邮件。
spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com
spring.mail.port=465
spring.mail.username=1351494395@qq.com
spring.mail.password=islthgvvkvwibaae
spring.mail.default-encoding=UTF-8
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.socketFactory.class=javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory
spring.mail.properties.mail.debug=true
#发送者
spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.from=1351494395@qq.com
#收件人
spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.to=384415765@qq.com
#抄送地址
spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.cc=384415765@qq.com
#忽略掉的事件
spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.ignore-changes=
14 项目构建与部署
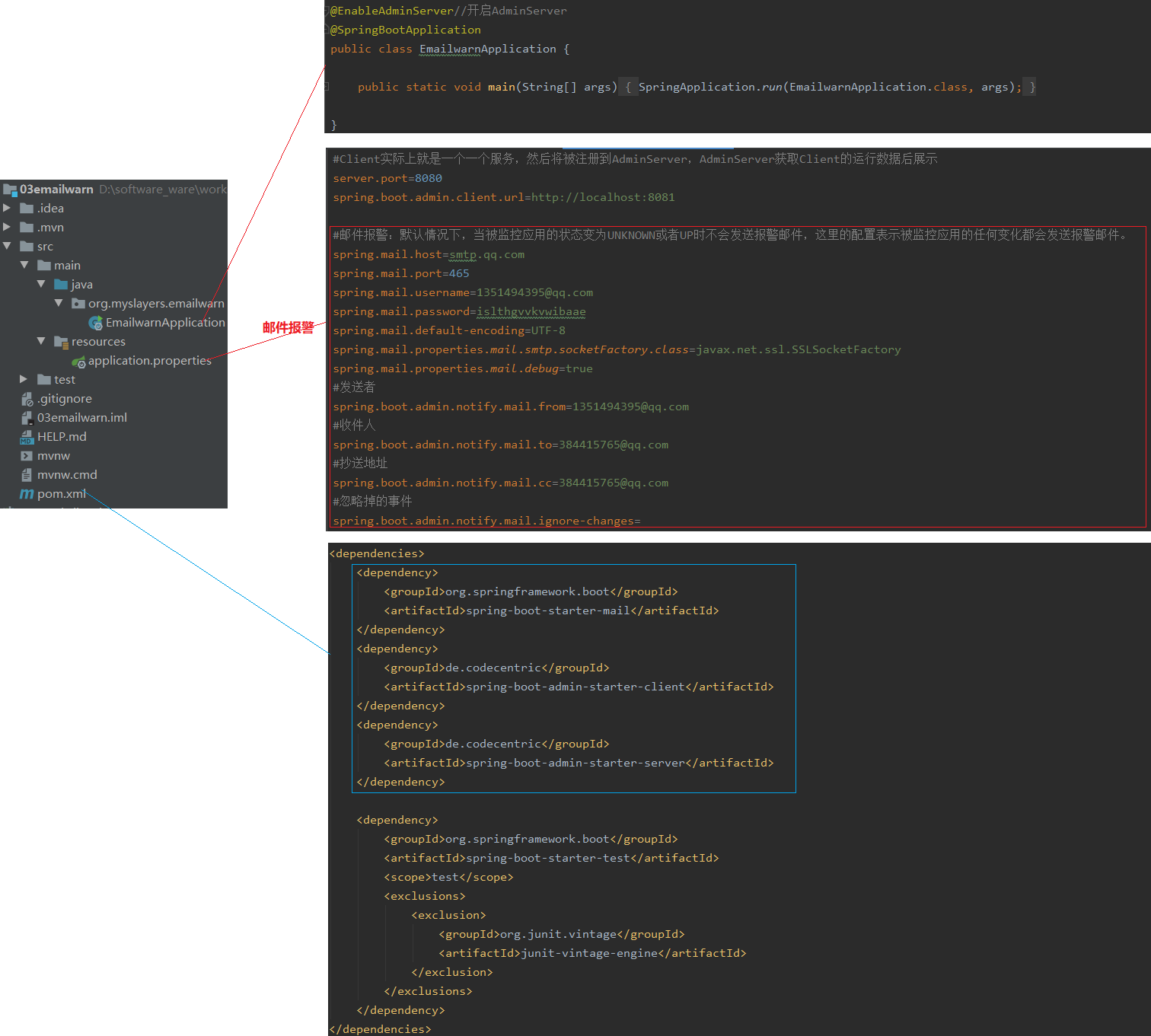
14.1 构建JAR
01.项目运行
a.Windows
java -jar jar-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
b.Linux
java -jar jar-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar & --&代表项目在后台运行
nohup java -jar jar-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar & --nohup当窗口关闭时服务不挂起,后台继续运行
02.一次打包两个jar
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<classifier>exec</classifier>
</configuration>
</plugin>
03.文件排除application.properties配置文件
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>lib</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>jar</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<classifier>lib</classifier>
<excludes>
<exclude>application.properties</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
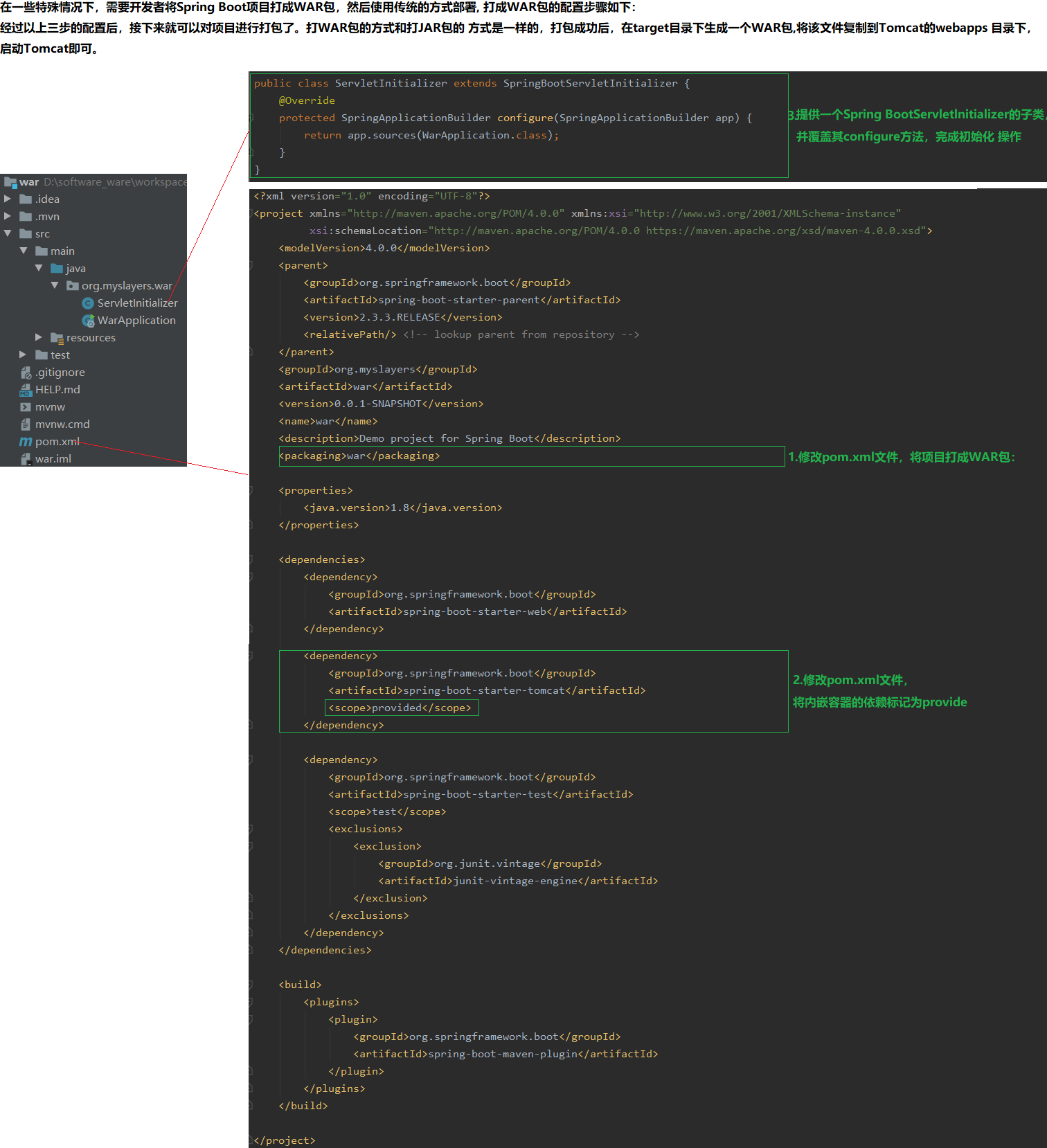
14.2 构建WAR
01.依赖
<groupId>org.myslayers</groupId>
<artifactId>war</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
02.配置
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder app) {
return app.sources(WarApplication.class);
}
}
15 Vhr
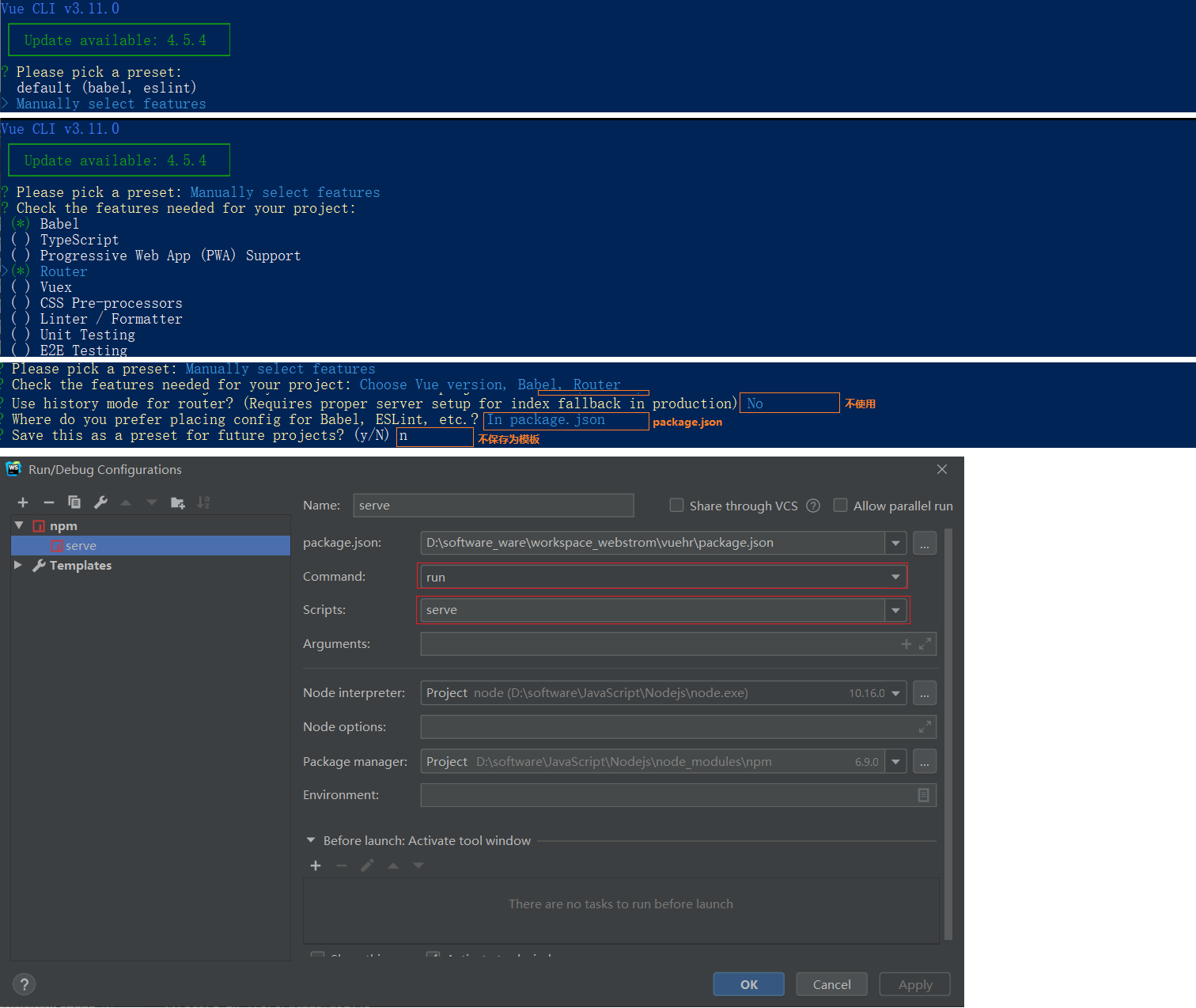
15.1 Vue-CLI 3:脚手架
01.安装Vue-CLI 3
a.淘宝镜像加速
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
b.安装vuecli脚手架
cnpm uninstall -g @vue/cli --卸载当前版本
cnpm install -g @vue/cli@3.11.0 --指定版本:3.11.0
c.检查vue版本
vue --version
02.创建工程项目(PowerShell,管理员身份打开)
a.解决报错,选择A或Y
set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
b.创建项目
cd D:\software_ware\workspace_webstrom
vue create vuehr
c.启动项目
npm run serve
03.依赖
a.element-ui
a.引入依赖
cnpm i element-ui -S
b.在主函数中加入element-ui(main.js)
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
Vue.use(ElementUI);
b.axios
a.引入依赖
cnpm install axios --save
b.使用(utils/api.js,配置路由表)
import axios from 'axios'
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: '登录页面',
component: Login,
hidden: true
},
});
c.在主函数中加入请求封装的方法(main.js)
import {postRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {postKeyValueRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {putRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {deleteRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {getRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {initMenu} from "./utils/menus"
Vue.prototype.postRequest = postRequest;
Vue.prototype.postKeyValueRequest = postKeyValueRequest;
Vue.prototype.putRequest = putRequest;
Vue.prototype.deleteRequest = deleteRequest;
Vue.prototype.getRequest = getRequest;
c.font-awesome
a.引入依赖
cnpm install font-awesome --save
b.使用(views/Home.vue,动态加载数据库中的iconCls字段)
<template slot="title">
<i style="color: #36acff; margin: 5px" :class="item.iconCls"></i>
<span>{{item.name}}</span>
</template>
c.在主函数中加入font-awesome(main.js)
import 'font-awesome/css/font-awesome.min.css'
d.vuex状态管理
a.引入依赖
npm install --save vuex
b.使用(store/index.js,对菜单项数据进行加载)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex);
c.在Vue实例中挂载store实例(main.js)
import store from './store'
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
e.vue-router
a.引入依赖
npm install vue-router --save
b.使用(router/index.js)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Router);
c.在Vue实例中挂载router实例(main.js)
import router from './router'
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
d.全局前置守卫
https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/advanced/navigation-guards.html
15.2 element-ui:桌面组件库
01.element-ui
a.引入依赖
cnpm i element-ui -S
b.在主函数中加入element-ui(main.js)
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
Vue.use(ElementUI, {size:'mini'}); --全局字体为mini
15.3 axios:前端请求封装为插件
01.axios
a.引入依赖
cnpm install axios --save
b.使用(utils/api.js,注册为插件)
import axios from 'axios'
export const postRequest = (url, params) => {
return axios({
method: 'post',
url: `${base}${url}`,
data: params
});
};
c.在主函数中加入请求封装的方法(main.js)
import {postRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {postKeyValueRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {putRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {deleteRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {getRequest} from "./utils/api";
import {initMenu} from "./utils/menus"
Vue.prototype.postRequest = postRequest;
Vue.prototype.postKeyValueRequest = postKeyValueRequest;
Vue.prototype.putRequest = putRequest;
Vue.prototype.deleteRequest = deleteRequest;
Vue.prototype.getRequest = getRequest;
02.开发插件(https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/plugins.html),插件通常用来为 Vue 添加全局功能。插件的功能范围没有严格的限制,一般有下面几种:本次采用第4中方式
①添加全局方法或者 property。如:vue-custom-element
②添加全局资源:指令/过滤器/过渡等。如 vue-touch
③通过全局混入来添加一些组件选项。如 vue-router
④添加 Vue 实例方法,通过把它们添加到 Vue.prototype 上实现。
⑤一个库,提供自己的 API,同时提供上面提到的一个或多个功能。如 vue-router
15.4 font-awesome:图标字体库
01.font-awesome
a.引入依赖
cnpm install font-awesome --save
b.使用(views/Home.vue,动态加载数据库中的iconCls字段)
<template slot="title">
<i style="color: #36acff; margin: 5px" :class="item.iconCls"></i>
<span>{{item.name}}</span>
</template>
c.在主函数中加入font-awesome(main.js)
import 'font-awesome/css/font-awesome.min.css'
15.5 vuex:状态管理,加载菜单项
01.vuex状态管理
a.引入依赖
npm install vuex --save
b.使用(store/index.js,对菜单项数据进行加载)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex);
c.在Vue实例中挂载store实例(main.js)
import store from './store'
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
15.6 vue-router:路由管理器
01.vue-router
a.引入依赖
npm install axios --save
b.使用(router.js,路由表)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Router);
import Login from '../views/Login.vue'
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: '登录页面',
component: Login,
hidden: true
},
});
c.在Vue实例中挂载router实例(main.js)
import router from './router'
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
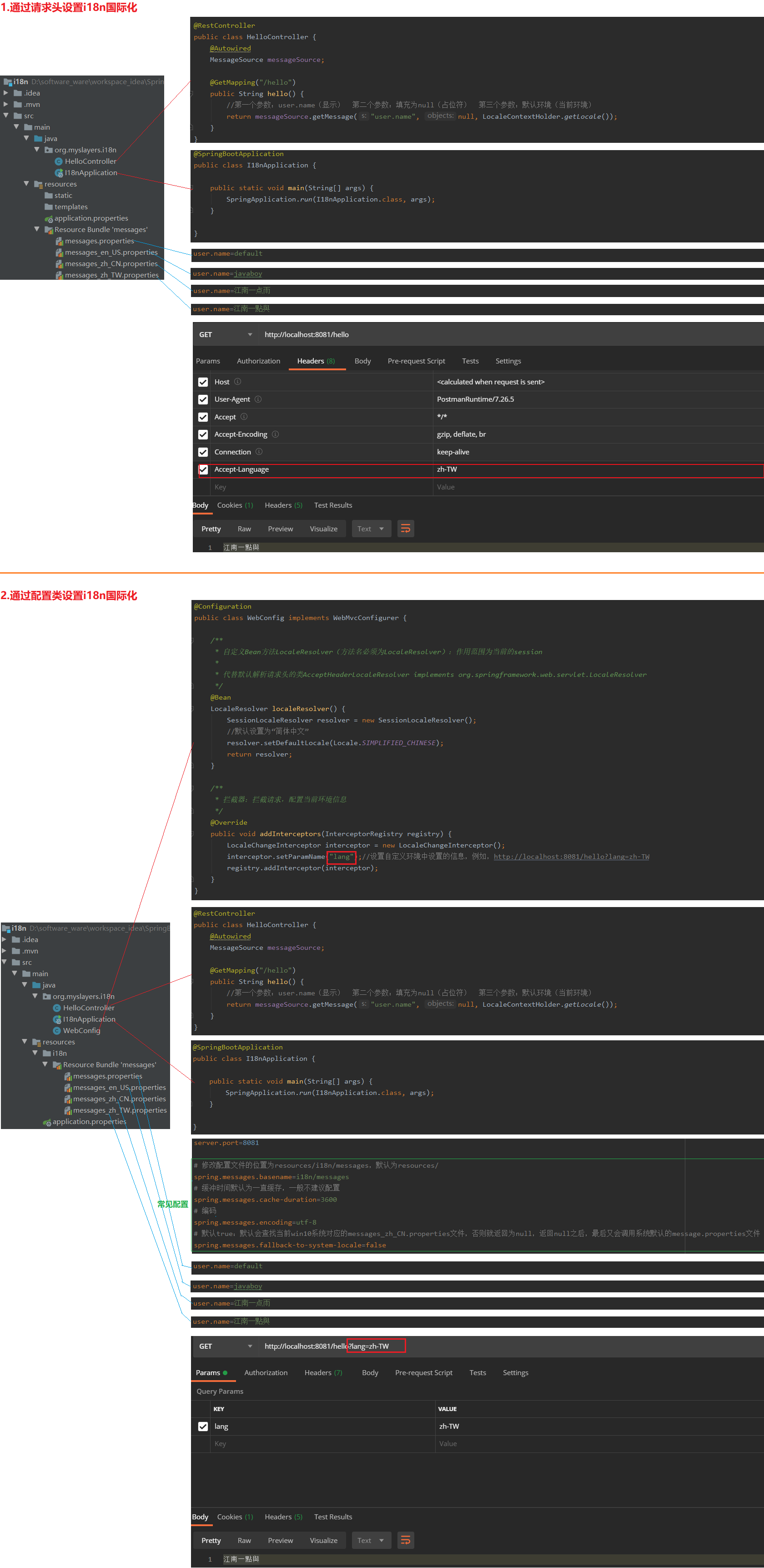
15.7 i18n:国际化
15.8 RabbitMQ + Task:保证消息可靠性
01.RabbitMQ
发送msg时,如果系统发生异常,不会立即删除该msg(区别于多线程,中间件可以保证消息不会丢失)
如果系统不再发生异常(例如,重启服务器),此时若检测到之前未发送成功的msg,会再次发送该msg
02.后端
Task定时发送消息时,轮询结束后找到需要重新投递的消息,来保证RabbitMQ发送消息的可靠性
但是,在重新投递消息时,可能会发生“同一条消息被发送多次的情况”
可采用“幂等性”的方式(例如,Redis来存储标识此msg的唯一标识UUID)